Page 201 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 201
V
Chapter 3 Scientific principles
I R
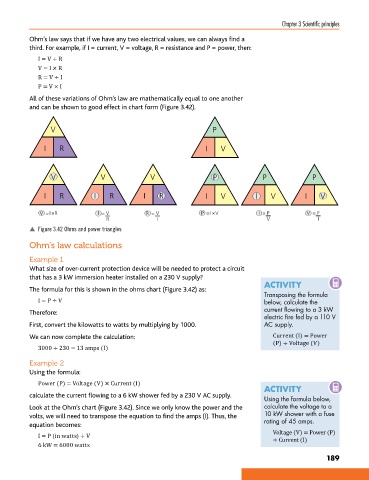
Ohm’s law says that if we have any two electrical values, we can always find a
third. For example, if I = current, V = voltage, R = resistance and P = power, then:
V V V
I = V ÷ R
V = I × R
I R I R I R
R = V ÷ I
P = V × I
V = I R I = V R = V
All of these variations of Ohm’s law are mathematically equal to one another R I
and can be shown to good effect in chart form (Figure 3.42).
V P
I R I V
V V V P P P
I R I R I R I V I V I V
V = I R I = V R = V P = I V I = P V = P
R I V I
p Figure 3.42 Ohms and power triangles
Ohm’s law calculations
P
Example 1
I
V
What size of over-current protection device will be needed to protect a circuit
that has a 3 kW immersion heater installed on a 230 V supply?
ACTIVITY
The formula for this is shown in the ohms chart (Figure 3.42) as:
P P P Transposing the formula
I = P ÷ V below, calculate the
Therefore: current flowing to a 3 kW
I V I V I V electric fire fed by a 110 V
First, convert the kilowatts to watts by multiplying by 1000. AC supply.
P = I V I = P V = P
We can now complete the calculation: I Current (I) = Power
V
(P) ÷ Voltage (V)
3000 ÷ 230 = 13 amps (I)
Example 2
Using the formula:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) × Current (I)
ACTIVITY
calculate the current flowing to a 6 kW shower fed by a 230 V AC supply.
Using the formula below,
Look at the Ohm’s chart (Figure 3.42). Since we only know the power and the calculate the voltage to a
volts, we will need to transpose the equation to find the amps (I). Thus, the 10 kW shower with a fuse
equation becomes: rating of 45 amps.
Voltage (V) = Power (P)
I = P (in watts) ÷ V
÷ Current (I)
6 kW = 6000 watts
189
9781510416482.indb 189 29/03/19 8:55 PM