Page 157 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 157
Fluid Flow 141
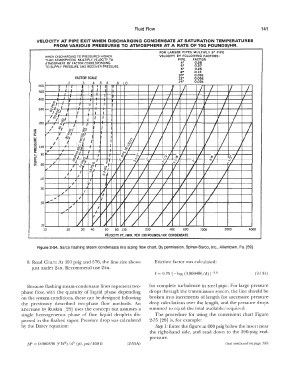
VELOCITY AT PIPE EXIT WHEN DISCHARGING CONDENSATE AT SATURATION TEMPERATURES
FROM VARIOUS PRESSURES TO ATMOSPHERE AT A RATE OF 100 POUNDS/HR.
FOR LARGER PIPES MULTIPLY 3' PIPE
WHEN DISCHARGING TO PRESSURES HIGHER VELOCITY BV FOLLOWING FACTORS:
THAN ATMOSPHERIC, MULTIPLY VELOCITY TO PIPE FACTOR
ATMOSPHERE BY FACTOR CORRESPONDING 4' 0.58
TO SUPPLY PRESSURE ANO RECEIVER PRESSURE. 5• 0.37
6' 0.25
8' 0.15
10• 0.095
FACTOR SCAL£ 12' 0.066
l 2 3 4 5 6 8 1 0 14' 0.054
600 I : I I . I I . . II I I I I I I
I
I
500 . ' I I I I I 7 I
. • T r I I 1 7
400 C., ' I ' I I I I I I I I
�.Q .... . I I . I I , I I I I
-f·
J
300 -&./-c., I I I I J J I I I I
I f'fl ,
0
, �,
I v;I �/ • I . I I I I I I 'T I
200 j I I ' v
/ �, �, _;, l I I I I I I J 7 /
I
�,-
.. I �· fl j I, I v / I I l I
!:JI
ti I
, / , I CJ° . I I I � I '
, _, �I I I 7 y.._. I I I 1 I 1 ' [/ I
I
�I
I
/§ j
I
¢ ... .::$j -·
r v
�L"'
�I
�I
n;)-
=, �/ I I I I ,; 1- :t/-- ...;� rt, -°O' .......... ..... , L fl ... /
O
s
/ -f:2,- .....
e '
/ . I :;;,:-- e -· v I I/ I I I
;� �I- 1-t I I '
' . I j ">' v I !/ I J I v I
40 I
J , I I I ) / / I / /
, r I I / / / f / J
30
/
.,,, / / .I I / j / , / /
, J[ I v v 7
_ ... � / , / / )
20 ' ., 7 v 7
., .,,, J . I / I / /: / / ,
J
, I 7 I / /
J '/ // 1// / / / I
10 60 "
JO 20 30 40 80 100 200 400 600 1000 2000 4000
VELOCITY FT./MIN. PER 100 POUNDS/HR. CONDENSATE
Figure 2-54. Sarco flashing steam condensate line sizing flow chart. By permission, Spirax-Sarco, Inc., Allentown, Pa. [59].
9. Read Chart: At 450 psig and 576, the line size shows Friction factor was calculated:
just under 2-in. Recommend use 2-in.
f = 0.25 [ -log (0.000486/d) 1- 20 (2-135)
Because flashing steam-condensate lines represent two- for complete turbulence in steel pipe. For large pressure
phase flow, with the quantity of liquid phase depending drops through the transmission system, the line should be
on the system conditions, these can be designed following broken into increments of length for successive pressure
the previously described two-phase flow methods. An drop calculations over the length, and the pressure drops
alternate by Ruskin [28) uses the concept but assumes a summed to equal the total available/required.
single homogeneous phase of fine liquid droplets dis- The procedure for using the convenient chart Figure
persed in the flashed vapor. Pressure drop was calculated 2-55 [28] is, for example:
by the Darcy equation: Step 1: Enter the figure at 600 psig below the insert near
the right-hand side, and read down to the 200-psig end-
pressure .
5
.!lP = 0.000336 (f\,\,'2)/d (p), psi/100 ft (2-55A) (text continued on page 153)