Page 155 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 155
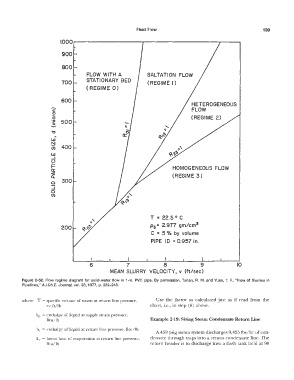
Fluid Flow 139
1000
900
800
FLOW WITH A SALTATION FLOW
700 STATIONARY BED (REGIME I)
( REGIME O)
- 600 HETEROGENEOUS
FLOW
c
0
�
- 500 (REGIME 2)
-�
E
,:,
�
w
�
Cl) 400
w
..J
o
i=
a:: HOMOGENEOUS FLOW
� (REGIME 3)
a 300
..J
0
Cl)
T = 22.5 ° C
200 Ps = 2.977 gm/cm 3
C = 5 % by volume
PIPE ID = 0.957 in.
6 7 8 9 10
MEAN SLURRY VELOCITY, v (ft/sec)
Figure 2-52. Flow regime diagram for solid-water flow in 1-in. PVC pipe. By permission, Turian, R. M. and Yuan, T. F., "Flow of Slurries in
Pipelines," A.I.Ch.E. Journal, vol. 23, 1977, p. 232-243.
where V = specific volume of steam at return line pressure, Use the factor so calculated just as if read from the
Ci: ft/lb chart, i.e., in step (8) above.
hp = enthalpy of liquid at supply steam pressure,
Btu/lb Example 2-19: Sizing Steam Condensate Return Line
hr = enthalpy of liquid at return line pressure, Btu/lb
A 450 psig steam system discharges 9,425 lbs/hr of con-
L, = latent heat of evaporation at return line pressure, densate through traps into a return condensate line. The
Btu/lb return header is to discharge into a flash tank held at 90