Page 221 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 221
Pumping of Liquids 191
Example 3-5: NPSH Available in Open Vessel Not at Sea Then: NPSH available= S + (P 2 - P,'P)(2.31/SpGr) - hsL
Level, Use Figure 3-39 = -8 + (60 - 44) (2.31/0.58) - 12 = +43.8 feet (3-10)
Conditions: vessel is at altitude 1500 ft, where atmos- This presents no pumping problem.
pheric pressure is 13.92 psia = Pa,
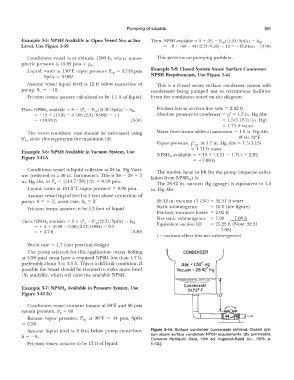
Example 3-8: Closed System Steam Surface Condenser
Liquid: water at 150°F, vapor pressure P"P = 3.718 psia
SpGr = 0.982 NPSH Requirements, Use Figure 3-44
Assume vessel liquid level is 12 ft below centerline of This is a closed steam surface condenser system with
pump, SL= -12. condensate being pumped out to retreatment facilities.
Friction losses: assume calculated to be 1.1 ft of liquid. From the conditions noted on the diagram,
Then: NPSHA available = S + (Pa - Pvp) (2.31/SpGr) - hsL Friction loss in suction line side = 2.92 ft
= -12 + (13.92 - 3.718) (2.31/0.982) - 1.1 Absolute pressure in condenser= p' = 1.5 in. Hg Abs
= + 10.88 ft (3-10) = 1.5(1.13 ft/in. Hg)
= 1.71 ft water
The worst condition case should be calculated using Water from steam tables at saturation = 1.5 in. Hg Abs
S' L, since this represents the maximum lift. @ 91.72°F
Vapor pressure, p'vp, at 1.5 in. Hg Abs= l.5(1.13)
= 1. 71 ft water
Example 3-6: NPSH Available in Vacuum System, Use NPSH..,. available= + 10 + (1.71 - 1.71) - 2.92
Figure 3-41A
= +7.08 ft
Conditions: vessel is liquid collector at 28 in. Hg Vacu- The suction head or lift for the pump (separate calcu-
um (referred to a 30 in. barometer). This is 30 - 28 = 2 lation from NPSHA) is:
in. Hg abs, or Pa = [ ( 14. 7 /30)] (2) = 0.98 psia.
The 28.42 in. vacuum Hg (gauge) is equivalent to 1.5
Liquid: water at 101.2°F, vapor pressure = 0.98 psia. in. Hg Abs
Assume vessel liquid level is 5 feet above centerline of
pump, S = + 5', worst case, S,,. = 2' 28.42 in. vacuum (1.137) = 32.31 ft water
Static submergence = JO.O (see figure)
Friction losses: assume to be 0.3 foot of liquid
Friction zentrance losses = 2.92 ft
Net static submergence = 7.08 7.08 ft
Then: NPSHA available = S + (Pa - P,p) (2.31/SpGr) - hsL Equivalent suction lift = 25.23 ft [Note: 32.31
= + 5 + (0.98 - 0.98) (2.31/0.994) - 0.3
= + 4.7 ft (3-10) - 7.08]
( = vacuum effect less net submergence)
Worst case = l. 7 (not practical design)
The pump selected for this application (water boiling CONDENSER
at 0.98 psia) must have a required NPSH less than 4. 7 ft,
preferably about 3 tc 3.5 ft. This is a difficult condition. If Abs E 1.50" Hg
possible the vessel should be elevated to make more head Vacuum = 28.42" Hg
(S) available, which will raise the available NPSH.
Condensate
Example 3-7: NPSHA Available in Pressure System, Use 91.72° F
Figure 3-41 (b)
Conditions: vessel contains butane at 90°F and 60 psia
system pressure. Pa= 60 -
Butane vapor pressure, P,p at 90°F = L!4 psia, SpGr
= 0.58.
Assume liquid level is 8 feet below pump centerline, Figure 3-44. Surface condenser condensate removal. Closed sys-
S = -8. tem steam surface condenser NPSH requirements. (By permission,
Cameron Hydraulic Data, 16th ed. Ingersoll-Rand Co., 1979, p.
Friction losses: assume to be 12 ft of liquid. 1-12.)