Page 50 - Template Tesis UTM v2.0
P. 50
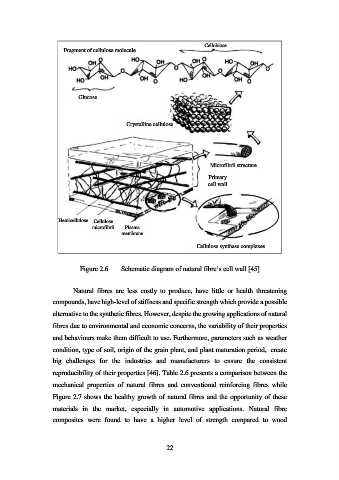
Cellobiose
Fragment of cellulose molecule
Glucose
Crystalline cellulose
Microfibril structure
Primary
cell wall
Hemicellulose Cellulose
microfibril Plasma
membrane
Cellulose synthase complexes
Figure 2.6 Schematic diagram of natural fibre’s cell wall [45]
Natural fibres are less costly to produce, have little or health threatening
compounds, have high-level of stiffness and specific strength which provide a possible
alternative to the synthetic fibres. However, despite the growing applications of natural
fibres due to environmental and economic concerns, the variability of their properties
and behaviours make them difficult to use. Furthermore, parameters such as weather
condition, type of soil, origin of the grain plant, and plant maturation period, create
big challenges for the industries and manufacturers to ensure the consistent
reproducibility of their properties [46]. Table 2.6 presents a comparison between the
mechanical properties of natural fibres and conventional reinforcing fibres while
Figure 2.7 shows the healthy growth of natural fibres and the opportunity of these
materials in the market, especially in automotive applications. Natural fibre
composites were found to have a higher level of strength compared to wood
22