Page 136 - Softcopy for Teachers buku kerja + nota Nilam Publications
P. 136
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
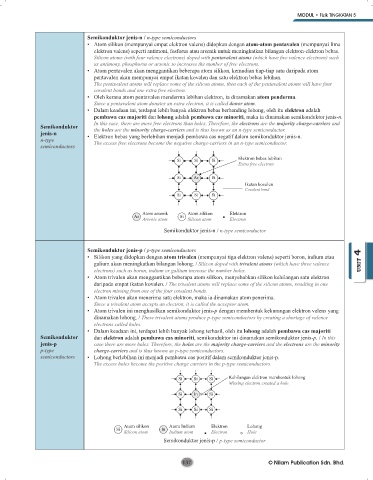
Semikonduktor jenis-n / n-type semiconductors
• Atom silikon (mempunyai empat elektron valens) didopkan dengan atom-atom pentavalen (mempunyai lima
elektron valens) seperti antimoni, fosforus atau arsenik untuk meningkatkan bilangan elektron-elektron bebas.
Silicon atoms (with four valence electrons) doped with pentavalent atoms (which have five valence electrons) such
as antimony, phosphorus or arsenic to increases the number of free electrons.
• Atom pentavalen akan menggantikan beberapa atom silikon, kemudian tiap-tiap satu daripada atom
pentavalen akan mempunyai empat ikatan kovalen dan satu elektron bebas lebihan.
The pentavalent atoms will replace some of the silicon atoms, then each of the pentavalent atoms will have four
covalent bonds and one extra free electron.
• Oleh kerana atom pentavalen menderma lebihan elektron, ia dinamakan atom penderma.
Since a pentavalent atom donates an extra electron, it is called donor atom.
• Dalam keadaan ini, terdapat lebih banyak elektron bebas berbanding lohong, oleh itu elektron adalah
pembawa cas majoriti dan lohong adalah pembawa cas minoriti, maka ia dinamakan semikonduktor jenis-n.
In this case, there are more free electrons than holes. Therefore, the electrons are the majority charge-carriers and
Semikonduktor the holes are the minority charge-carriers and is thus known as an n-type semiconductor.
jenis-n • Elektron bebas yang berlebihan menjadi pembawa cas negatif dalam semikonduktor jenis-n.
n-type The excess free electrons become the negative charge-carriers in an n-type semiconductor.
semiconductors
Si Si Si Elektron bebas lebihan
Extra free electron
Si As Si
Ikatan kovalen
Covalent bond
Si Si Si
Atom arsenik Atom silikon Elektron
As Si
Arsenic atom Silicon atom Electron
Semikonduktor jenis-n / n-type semiconductor
Semikonduktor jenis-p / p-type semiconductors
• Silikon yang didopkan dengan atom trivalen (mempunyai tiga elektron valens) seperti boron, indium atau
galium akan meningkatkan bilangan lohong. / Silicon doped with trivalent atoms (which have three valence UNIT 4
electrons) such as boron, indium or gallium increase the number holes.
UNIT 4
• Atom trivalen akan menggantikan beberapa atom silikon, menyebabkan silikon kehilangan satu elektron
daripada empat ikatan kovalen. / The trivalent atoms will replace some of the silicon atoms, resulting in one
electron missing from one of the four covalent bonds.
• Atom trivalen akan menerima satu elektron, maka ia dinamakan atom penerima.
Since a trivalent atom accepts an electron, it is called the acceptor atom.
• Atom trivalen ini menghasilkan semikonduktor jenis-p dengan membentuk kekurangan elektron valens yang
dinamakan lohong. / These trivalent atoms produce p-type semiconductors by creating a shortage of valence
electrons called holes.
• Dalam keadaan ini, terdapat lebih banyak lohong terhasil, oleh itu lohong adalah pembawa cas majoriti
Semikonduktor dan elektron adalah pembawa cas minoriti, semikonduktor ini dinamakan semikonduktor jenis-p. / In this
jenis-p case there are more holes. Therefore, the holes are the majority charge-carriers and the electrons are the minority
p-type charge-carriers and is thus known as p-type semiconductors.
semiconductors • Lohong berlebihan ini menjadi pembawa cas positif dalam semikonduktor jenis-p.
The excess holes become the positive charge carriers in the p-type semiconductors.
Si Si Si Kehilangan elektron membentuk lohong
Missing electron created a hole
Si In Si
Si Si Si
Atom silikon Atom Indium Elektron Lohong
Si Silicon atom In Indium atom Electron Hole
Semikonduktor jenis-p / p-type semiconductor
137 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.