Page 138 - Softcopy for Teachers buku kerja + nota Nilam Publications
P. 138
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
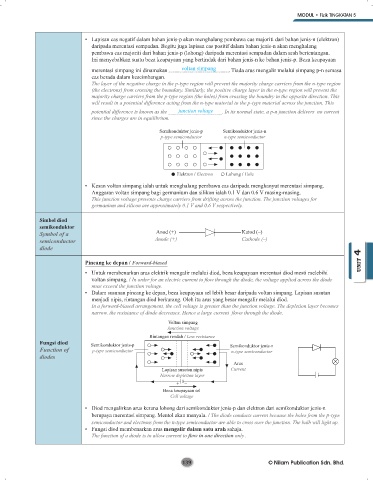
• Lapisan cas negatif dalam bahan jenis-p akan menghalang pembawa cas majoriti dari bahan jenis-n (elektron)
daripada merentasi sempadan. Begitu juga lapisan cas positif dalam bahan jenis-n akan menghalang
pembawa cas majoriti dari bahan jenis-p (lohong) daripada merentasi sempadan dalam arah bertentangan.
Ini menyebabkan suatu beza keupayaan yang bertindak dari bahan jenis-n ke bahan jenis-p. Beza keupayaan
merentasi simpang ini dinamakan voltan simpang . Tiada arus mengalir melalui simpang p-n semasa
cas berada dalam keseimbangan.
The layer of the negative charge in the p-type region will prevent the majority charge carriers from the n-type region
(the electrons) from crossing the boundary. Similarly, the positive charge layer in the n-type region will prevent the
majority charge carriers from the p-type region (the holes) from crossing the boundry in the opposite direction. This
will result in a potential difference acting from the n-type material to the p-type material across the junction. This
potential difference is known as the junction voltage . In its normal state, a p-n junction delivers no current
since the charges are in equilibrium.
Semikonduktor jenis-p Semikonduktor jenis-n
p-type semiconductor n-type semiconductor
Elektron / Electron Lohong / Hole
• Kesan voltan simpang ialah untuk menghalang pembawa cas daripada menghanyut merentasi simpang.
Anggaran voltan simpang bagi germanium dan silikon ialah 0.1 V dan 0.6 V masing-masing.
This junction voltage prevents charge carriers from drifting across the junction. The junction voltages for
germanium and silicon are approximately 0.1 V and 0.6 V respectively.
Simbol diod
semikonduktor
Symbol of a Anod (+) Katod (–)
semiconductor Anode (+) Cathode (–)
diode
Pincang ke depan / Forward-biased UNIT 4
• Untuk membenarkan arus elektrik mengalir melalui diod, beza keupayaan merentasi diod mesti melebihi
UNIT 4
voltan simpang. / In order for an electric current to flow through the diode, the voltage applied across the diode
must exceed the junction voltage.
• Dalam susunan pincang ke depan, beza keupayaan sel lebih besar daripada voltan simpang. Lapisan susutan
menjadi nipis, rintangan diod berkurang. Oleh itu arus yang besar mengalir melalui diod.
In a forward-biased arrangement, the cell voltage is greater than the junction voltage. The depletion layer becomes
narrow, the resistance of diode decreases. Hence a large current flows through the diode.
Voltan simpang
Junction voltage
Rintangan rendah / Low resistance
Fungsi diod Semikonduktor jenis-p Semikonduktor jenis-n
Function of p-type semiconductor n-type semiconductor
diodes
Arus
Lapisan susutan nipis Current
Narrow depletion layer
+ –
Beza keupayaan sel
Cell voltage
• Diod mengalirkan arus kerana lohong dari semikonduktor jenis-p dan elektron dari semikonduktor jenis-n
berupaya merentasi simpang. Mentol akan menyala. / The diode conducts current because the holes from the p-type
semiconductor and electrons from the n-type semiconductor are able to cross over the junction. The bulb will light up.
• Fungsi diod membenarkan arus mengalir dalam satu arah sahaja.
The function of a diode is to allow current to flow in one direction only .
139 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.