Page 762 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 762
which are beyond the scope of the CISSP exam. However, you should
be familiar with the details of the flags field. The flags field can contain
a designation of one or more flags, or control bits. These flags indicate
the function of the TCP packet and request that the recipient respond
in a specific manner. The flags field is 8 bits long. Each of the bit
positions represents a single flag, or control setting. Each position can
be set on with a value of 1 or off with a value of 0. There are some
conditions in which multiple flags can be enabled at once (in other
words, the second packet in the TCP three-way handshake when both
the SYN and ACK flags are set). Table 11.2 details the flag control bits.
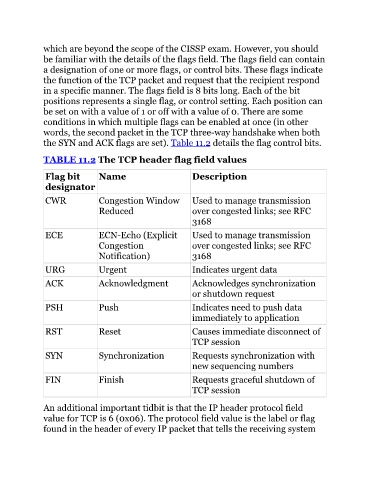
TABLE 11.2 The TCP header flag field values
Flag bit Name Description
designator
CWR Congestion Window Used to manage transmission
Reduced over congested links; see RFC
3168
ECE ECN-Echo (Explicit Used to manage transmission
Congestion over congested links; see RFC
Notification) 3168
URG Urgent Indicates urgent data
ACK Acknowledgment Acknowledges synchronization
or shutdown request
PSH Push Indicates need to push data
immediately to application
RST Reset Causes immediate disconnect of
TCP session
SYN Synchronization Requests synchronization with
new sequencing numbers
FIN Finish Requests graceful shutdown of
TCP session
An additional important tidbit is that the IP header protocol field
value for TCP is 6 (0x06). The protocol field value is the label or flag
found in the header of every IP packet that tells the receiving system