Page 108 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 108
VISCOSE FIBRE 97
Because of its lower DP and crystallinity, and higher accessibility, viscose even
tends to be reactive under conditions where cotton is quite stable. For example,
cold, concentrated or hot dilute NaOH solution will attack and tend to dissolve
viscose, so it requires milder processing conditions. Viscose also has a higher
number of carboxylate groups than cotton and will absorb cationic dyes by ion
exchange.
The composition of the aqueous coagulating bath significantly influences the
properties of the viscose filaments. A typical bath might contain dilute sulphuric
acid, sodium sulphate, glucose and zinc sulphate. The salts promote rapid
coagulation and dehydration of the coagulated sodium cellulose xanthate by
osmosis. The acid present in the bath catalyses hydrolysis of the cellulose xanthate
back to cellulose. Cellulose is generated either by transformation of the sodium
cellulose xanthate into cellulose xanthate, and its subsequent hydrolysis, or
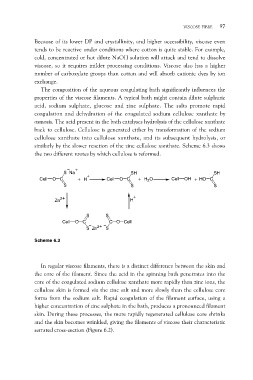
similarly by the slower reaction of the zinc cellulose xanthate. Scheme 6.3 shows
the two different routes by which cellulose is reformed.
S Na SH SH
Cell O C + H2O Cell OH + HO C
Cell O C +H
S S
S
H
Zn2
S S
C O Cell
Cell O C
S Zn2 S
Scheme 6.3
In regular viscose filaments, there is a distinct difference between the skin and
the core of the filament. Since the acid in the spinning bath penetrates into the
core of the coagulated sodium cellulose xanthate more rapidly than zinc ions, the
cellulose skin is formed via the zinc salt and more slowly than the cellulose core
forms from the sodium salt. Rapid coagulation of the filament surface, using a
higher concentration of zinc sulphate in the bath, produces a pronounced filament
skin. During these processes, the more rapidly regenerated cellulose core shrinks
and the skin becomes wrinkled, giving the filaments of viscose their characteristic
serrated cross-section (Figure 6.2).