Page 70 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 70
POLYESTERS 59
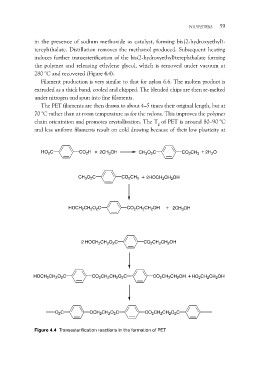
in the presence of sodium methoxide as catalyst, forming bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-
terephthalate. Distillation removes the methanol produced. Subsequent heating
induces further transesterification of the bis(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalate forming
the polymer and releasing ethylene glycol, which is removed under vacuum at
280 °C and recovered (Figure 4.4).
Filament production is very similar to that for nylon 6.6. The molten product is
extruded as a thick band, cooled and chipped. The blended chips are then re-melted
under nitrogen and spun into fine filaments.
The PET filaments are then drawn to about 4–5 times their original length, but at
70 °C rather than at room temperature as for the nylons. This improves the polymer
chain orientation and promotes crystallisation. The Tg of PET is around 80–90 °C
and less uniform filaments result on cold drawing because of their low plasticity at
HO2C CO2H + 2CH3OH CH3O2C CO2CH3 + 2H2O
CH3O2C CO2CH3 + 2HOCH2CH2OH
HOCH2CH2O2C CO2CH2CH2OH + 2CH3OH
2 HOCH2CH2O2C CO2CH2CH2OH
HOCH2CH2O2C CO2CH2CH2O2C CO2CH2CH2OH +HO2CH2CH2OH
O2C OCH2CH2O2C CO2CH2CH2O2C
Figure 4.4 Transesterification reactions in the formation of PET