Page 104 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 104
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts]
ͳǤͶǤʹ ϐ
ǣ
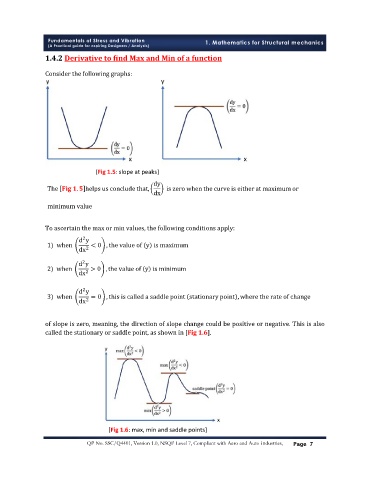
[Fig 1.5: slope at peaks]
dy
The . helps us conclude that, is zero when the curve is either at maximum or
dx
minimum value
ǡ
ǣ
2
d y
1) when < 0 , the value of y is maximum
dx 2
2
d y
2) when > 0 , the value of y is minimum
dx 2
2
d y
3) when = 0 , this is called a saddle point stationary point , where the rate of change
dx 2
ǡ ǡ
Ǥ
ǡ ȏ ͳǤȐǤ
[Fig 1.6: max, min and saddle points]
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries, Page 7