Page 106 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 106
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts]
ʹǣ
ȋȏ ͳǤͺȐȌ ȋ ȌǤ
ʹǣ
ȏ ͳǤͺȐǤ
Ǯǯǡ Ǯǯ ǮǯǤ
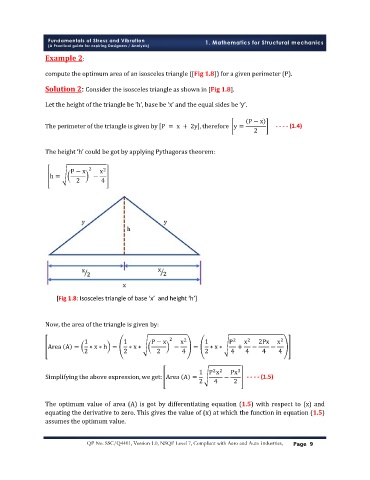
P − x
The perimeter of the triangle is given by P = x + 2y , therefore y = - - - - (1.4)
2
Ǯǯ
ǣ
P − x 2 x 2
h = −
2 4
[Fig 1.8: Isosceles triangle of base ‘x’ and height ‘h’]
ǡ ǣ
1 1 P − x 2 x 2 1 P 2 x 2 2Px x 2
Area A = ∗ x ∗ h = ∗ x ∗ − = ∗ x ∗ + − −
2 2 2 4 2 4 4 4 4
2 2
1 P x Px 3
Simplifying the above expression, we get: Area A = − - - - - (1.5)
2 4 2
ȋ Ȍ ȋͳǤͷȌ
ȋȌ
Ǥ ȋȌ
ȋͳǤͷȌ
Ǥ
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries, Page 9