Page 129 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 129
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts] 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
ϐǡ
ǡ
ǡ ǣ
a + b = 4i + 5j + 7i + 2j = 11i + 7j
The magnitude of the resultant vector is: 11 + 7 = 13.03
2
2
The direction of the resultant vector is given by:
7
0
−1
tan −1 = tan 0.6363 = 32.47 , with respect to the positive (x − axis)
11
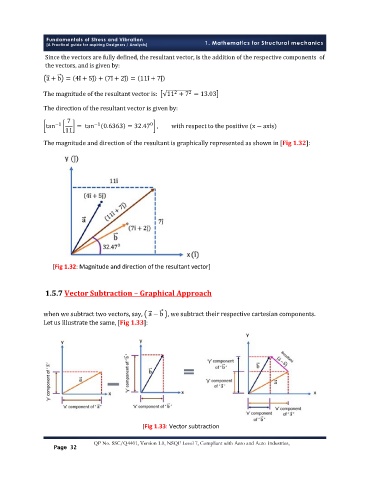
The magnitude and direction of the resultant is graphically represented as shown in [Fig 1.32]:
[Fig 1.32: Magnitude and direction of the resultant vector]
ͳǤͷǤ
–
when we subtract two vectors, say, a − b , we subtract their respective cartesian components.
Let us illustrate the same, [Fig 1.33]:
[Fig 1.33: Vector subtraction
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries,
Page 32