Page 74 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 74
Document Title
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration Chapter Title
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts] 2. Engineering Mechanics
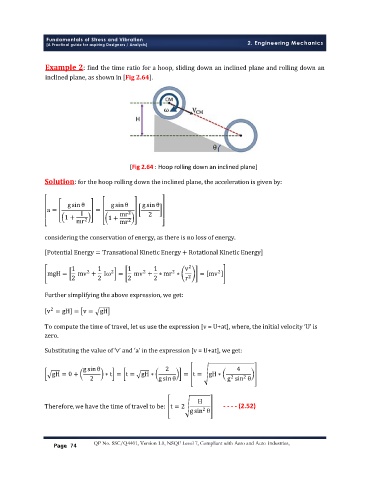
ʹǣ ϐ ǡ
ǡ ȏ ʹǤͶȐǤ
[Fig 2.64 : Hoop rolling down an inclined plane]
Solution: for the hoop rolling down the inclined plane, the acceleration is given by:
g sin θ g sinθ g sin θ
a = I = mr 2 2
1 + 2 1 + 2
mr mr
considering the conservation of energy, as there is no loss of energy.
Potential Energy = Transational Kinetic Energy + Rotational Kinetic Energy
1 1 1 1 v 2
2
2
2
2
2
mgH = mv + Iω = mv + ∗ mr ∗ = mv
2 2 2 2 r 2
Further simplifying the above expression, we get:
v = gH = v = gH
2
To compute the time of travel, let us use the expression [v = U+at], where, the initial velocity ‘U’ is
zero.
Substituting the value of ‘v’ and ‘a’ in the expression [v = U+at], we get:
g sin θ 2 4
gH = 0 + ∗ t = t = gH ∗ = t = gH ∗
2
2
2 g sin θ g sin θ
H
Therefore, we have the time of travel to be: t = 2 - - - - (2.52)
2
g sin θ
Page 74 QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries,