Page 115 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 115
10.2 Center of Mass 315
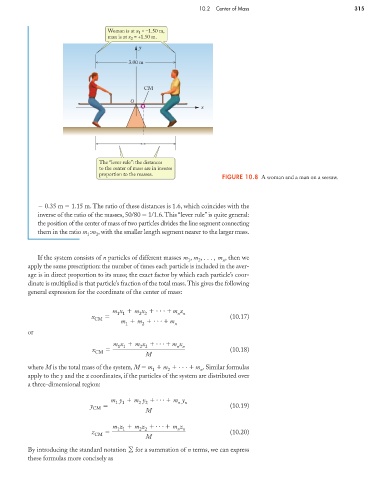
Woman is at x 1 = –1.50 m,
man is at x 2 = +1.50 m.
y
3.00 m
CM
O
x
The “lever rule”: the distances
to the center of mass are in inverse
proportion to the masses.
FIGURE 10.8 A woman and a man on a seesaw.
0.35 m 1.15 m. The ratio of these distances is 1.6, which coincides with the
inverse of the ratio of the masses, 50/80 1/1.6.This “lever rule” is quite general:
the position of the center of mass of two particles divides the line segment connecting
them in the ratio m :m , with the smaller length segment nearer to the larger mass.
1 2
If the system consists of n particles of different masses m , m ,..., m , then we
1 2 n
apply the same prescription: the number of times each particle is included in the aver-
age is in direct proportion to its mass; the exact factor by which each particle’s coor-
dinate is multiplied is that particle’s fraction of the total mass.This gives the following
general expression for the coordinate of the center of mass:
m x m x m x
n n
1 1
2 2
x (10.17)
CM
m m m n
1
2
or
m x m x m x
2 2
n n
1 1
x (10.18)
CM
M
where M is the total mass of the system, M m m ... m . Similar formulas
1 2 n
apply to the y and the z coordinates, if the particles of the system are distributed over
a three-dimensional region:
m y m y m y
1 1
n n
2 2
y CM (10.19)
M
m z m z m z
1 1
n n
2 2
z CM (10.20)
M
By introducing the standard notation g for a summation of n terms, we can express
these formulas more concisely as