Page 117 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 117
10.2 Center of Mass 317
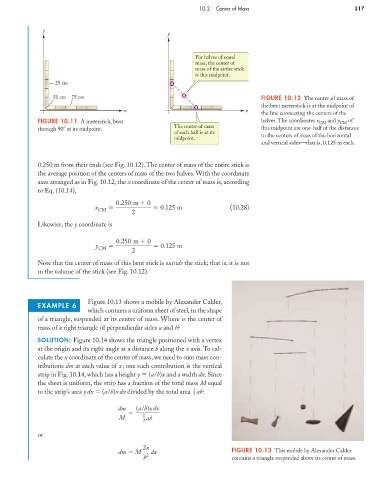
y
y
For halves of equal
mass, the center of
mass of the entire stick
is this midpoint.
25 cm
50 cm 75 cm FIGURE 10.12 The center of mass of
the bent meterstick is at the midpoint of
x x
the line connecting the centers of the
FIGURE 10.11 A meterstick, bent halves. The coordinates x CM and y CM of
The center of mass
through 90 at its midpoint. this midpoint are one-half of the distances
of each half is at its
midpoint. to the centers of mass of the horizontal
and vertical sides—that is, 0.125 m each.
0.250 m from their ends (see Fig. 10.12). The center of mass of the entire stick is
the average position of the centers of mass of the two halves. With the coordinate
axes arranged as in Fig. 10.12, the x coordinate of the center of mass is, according
to Eq. (10.14),
0.250 m 0
x 0.125 m (10.28)
CM
2
Likewise, the y coordinate is
0.250 m 0
y 0.125 m
CM
2
Note that the center of mass of this bent stick is outside the stick; that is, it is not
in the volume of the stick (see Fig. 10.12).
Figure 10.13 shows a mobile by Alexander Calder,
EXAMPLE 6
which contains a uniform sheet of steel, in the shape
of a triangle, suspended at its center of mass. Where is the center of
mass of a right triangle of perpendicular sides a and b?
SOLUTION: Figure 10.14 shows the triangle positioned with a vertex
at the origin and its right angle at a distance b along the x axis. To cal-
culate the x coordinate of the center of mass, we need to sum mass con-
tributions dm at each value of x; one such contribution is the vertical
strip in Fig. 10.14, which has a height y (a/b)x and a width dx. Since
the sheet is uniform, the strip has a fraction of the total mass M equal
1
to the strip’s area ydx (a/b)xdx divided by the total area ab:
2
dm (a/b)x dx
M 1 ab
2
or
2x FIGURE 10.13 This mobile by Alexander Calder
dm M 2 dx
b contains a triangle suspended above its center of mass.