Page 150 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 150
350 CHAPTER 11 Collisions
(a) After the collision is over, during the subsequent swinging motion of the pendu-
lum, the total mechanical energy (kinetic plus potential) is conserved. At the bottom
1 2
of the swing, the energy is kinetic, (m m )v ; and at the top of the swing at
2 1 2 CM
height h, it is potential, (m m )gh. Hence, conservation of the total mechanical
1 2
m 2 energy tells us that
m 1
1 2
2 (m m )v CM (m m )gh (11.23)
1
2
2
1
Momentum is conserved If we divide this by (m m ) and take the square root of both sides, we find
2
1
as bullet becomes stuck
in block. v 22gh (11.24)
CM
(b) Substitution of this into Eq. (11.22) yields
m v
1 1
22gh (11.25)
m m
1 2
which we can solve for v , with the result
1
h
m m 2
1
v 22gh
1 m
1
Mechanical energy is 0.0097 kg 4.0 kg
2
conserved as block 22 9.81 m s 0.19 m (11.26)
swings upward. 0.0097 kg
800 m s
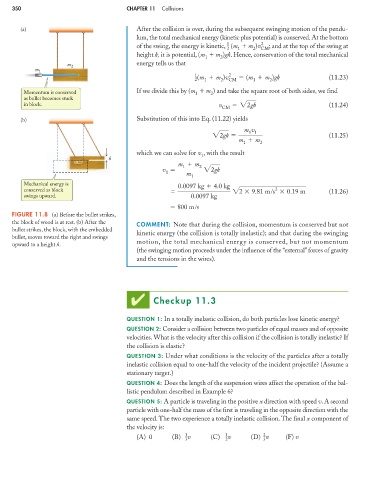
FIGURE 11.8 (a) Before the bullet strikes,
the block of wood is at rest. (b) After the
COMMENT: Note that during the collision, momentum is conserved but not
bullet strikes, the block, with the embedded
kinetic energy (the collision is totally inelastic); and that during the swinging
bullet, moves toward the right and swings
motion, the total mechanical energy is conserved, but not momentum
upward to a height h.
(the swinging motion proceeds under the influence of the “external” forces of gravity
and the tensions in the wires).
✔ Checkup 11.3
QUESTION 1: In a totally inelastic collision, do both particles lose kinetic energy?
QUESTION 2: Consider a collision between two particles of equal masses and of opposite
velocities. What is the velocity after this collision if the collision is totally inelastic? If
the collision is elastic?
QUESTION 3: Under what conditions is the velocity of the particles after a totally
inelastic collision equal to one-half the velocity of the incident projectile? (Assume a
stationary target.)
QUESTION 4: Does the length of the suspension wires affect the operation of the bal-
listic pendulum described in Example 6?
QUESTION 5: A particle is traveling in the positive x direction with speed v. A second
particle with one-half the mass of the first is traveling in the opposite direction with the
same speed.The two experience a totally inelastic collision.The final x component of
the velocity is:
1
2
1
(A) 0 (B) v (C) v (D) v (F) v
3
2
3