Page 243 - NAVAL SCIENCE 3 TEXTBOOK
P. 243
NAVAL WEAPONS AND AIRCRAFT 249
TARGET H-IGHTPATH
I
I ,
I I
I I I
I , I
I
0"
~
I I
I
I ~/<
I
I
., /
MISSILE FLIGHT PATH
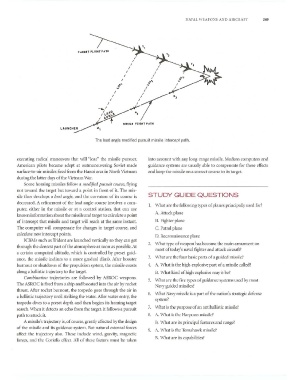
The lead angle modified pursuit missile intercept path.
execllting radical maneuvcrs that will "lose" the missile pursuer. into account with any long-range missile. i,,[odem computers and
American pilots became adept at outmaneuvering Soviet~made guidance systems are usually able to compensate for these effects
surface-to-air missiles fired from the Hanoi area in North Vietnam and keep the missile on a correct course to its target.
during the latter days of the Vietnam \Var.
Some homing missiles follow a modified pursuit course, flying
not toward the target but toward a point in front of it. The mis-
sile thus develops a lead angle, and the curvature of its course is STUDY GUIDE QUESTIONS
decreased. A refinement of the lead angle course involves a com-
I. \'Vh'1t arc the following types of planes principally used for?
puter, either in the missile or at a control station, that can use
tI. tlNack plane
known intormation about the missile and target to calculate a point
of intercept that missile and target will reach at the same instant. ll. Fighter plane
The computer will compensate tor changes in target course, and C. Patrol plane
calculate new intercept points.
D. Reconnaissance plant?
ICBI\·[s such as Trident are launched vertically so they can get
2. \Vhat type of weapon has become the main armament on
through the densest part of the atmosphere as soon as possible. At
most of to day's Ililval fighter and attack aircraft?
a certain computed i.1ititude, which is controlled by prcset gl1id~
3. \Vhat are the four basic Pi.uts of a guided missile?
ance, the missile inclines to il more gradual climb. After booster
burnout or shutdown of the propulsion s),stem, the missile coasts 4. A. \Vhat is the high-explosive part of a missile called?
along a ballistic trajector), to the target. ll. What kind of high explosive may it be'
Combillation trajectories are followed b)' ASROC weapons.
5. \·Vhat are the five types of guidance systems lIsed by most
The tlSROC is fired from a ship and boosted into the air b)' rocket
NeW)' guided missiles?
thrust. After rocket burnout, the torpedo goes through the air in
6. \Vhat Navy missile is a part of the nation's strategic defense
a ballistic trajectory until striking the water. After water entry, the
s),stem?
torpedo dives to a preset depth and then begins its homing target
7. \,Vhat is the purpose of an .mtiballistic missile?
search. \Vhen it detects an echo from the target, it follows a pursuit
path to aNack it. 8. A. \'Vhat is the Harpoon missile?
A missile's trajectory is, of course, greatly affected by the design B. \,Vhat are its principal features ilnd range?
of the missile and its guidance s),stem. But natural external forces
9. A. \Vhat is the Tomahawk missile?
affect the trajectory also. These include wind, gravity. magnetic
B. \,Vhat are its capabilities?
forces, and the Coriolis effect. All of these factors must be taken