Page 361 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 361
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 337
tion was compromised by limited sensitivity due to vestigated. In a rat model of autoimmune myocardi-
a weak signal from the valvular target region and tis, feasibility of [11C]-methionine-PET imaging for the
difficult localization of inflammatory foci. The speci- detection of cardiac inflammation could recently be
ficity of leukocyte scintigraphy with SPECT/CT could demonstrated. Methionine accumulation co-localized
be particularly useful when diagnostic uncertainty with histologically confirmed cardiac inflammatory le-
remains after echocardiography and FDGPET/ CT, sions and [18F]-FDG-uptake, indicating that [11C]-me-
especially in patients who have had cardiac surgery thionine-PET might represent a promising imaging
within the past 4 weeks. agent for the noninvasive diagnosis of myocarditis.
Another new approach needing further evaluation in-
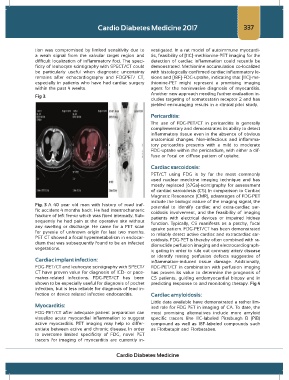
Fig 3.
cludes targeting of somatostatin receptor 2 and has
yielded encouraging results in a clinical pilot study.
Pericarditis:
The use of FDG-PET/CT in pericarditis is generally
complementary and demonstrates its ability to detect
inflammatory tissue even in the absence of obvious
anatomical changes. Non-infectious and inflamma-
tory pericarditis presents with a mild to moderate
FDG-uptake within the pericardium, with either a dif-
fuse or focal on diffuse pattern of uptake.
Cardiac sarcoidosis:
PET/CT using FDG is by far the most commonly
used nuclear medicine imaging technique and has
mostly replaced [67Ga]-scintigraphy for assessment
of cardiac sarcoidosis (CS). In comparison to Cardiac
Magnetic Resonance (CMR), advantages of FDG-PET
include the biologic nature of the imaging signal, the
Fig. 3 A 40 year old man with history of road traf- potential to identify cardiac and extra-cardiac sar-
fic accident 4 months back. He had intertrochanteric coidosis involvement, and the feasibility of imaging
fracture of left femur which was fixed internally. Sub- patients with electrical devices or impaired kidney
sequently he had pain at the operative site without function. Typically, CS manifests as a patchy, focal
any swelling or discharge. He came for a PET scan uptake pattern. FDG-PET/CT has been demonstrated
for pyrexia of unknown origin for last two months. to reliably detect active cardiac and extracardiac sar-
PET CT showed a focal hypermetabolism in endocar- coidosis. FDG-PET is thereby often combined with ra-
dium that was subsequently found to be an infected dionuclide perfusion imaging and electrocardiograph-
vegetations.
ic gating in order to rule out coronary artery disease
or identify resting perfusion defects suggestive of
Cardiac implant infection: inflammation-induced tissue damage. Additionally,
FDG-PET/CT and leukocyte scintigraphy with SPECT/ FDG-PET/CT in combination with perfusion imaging
CT have proven value for diagnosis of ICD- or pace- has proven its value to determine the prognosis of
maker-related infections. FDG-PET/CT has been CS patients, guiding endomyocardial biopsy and in
shown to be especially useful for diagnosis of pocket predicting response to and monitoring therapy. Fig 4
infection, but is less reliable for diagnosis of lead in-
fection or device related infective endocarditis. Cardiac amyloidosis:
Little data available have demonstrated a rather lim-
Myocarditis: ited role for FDG PET in imaging of CA. To date, the
FDG-PET/CT after adequate patient preparation can most promising alternatives include more amyloid
visualize acute myocardial inflammation to suggest specific tracers like 11C-labeled Pittsburgh B (PiB)
active myocarditis. PET imaging may help to differ- compound as well as 18F-labeled compounds such
entiate between active and chronic disease. In order as Florbetapir and Florbetaben.
to overcome limited specificity of FDG, novel PET
tracers for imaging of myocarditis are currently in-
Cardio Diabetes Medicine