Page 605 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 605
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 581
Exercise is extreme cold or heat to be avoided
Inspection of feet before and after exercise is necessary
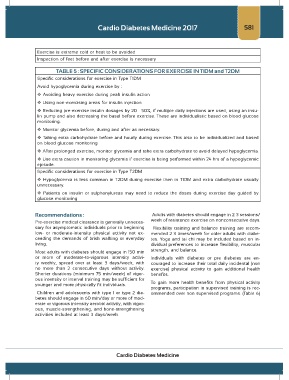
TABLE 5 : SPECIFIC CONSIDERATIONS FOR EXERCISE IN T1DM and T2DM
Specific considerations for exercise in Type T1DM
Avoid hypoglycemia during exercise by :
Avoiding heavy exercise during peak insulin action
Using non-exercising areas for insulin injection
Reducing pre-exercise insulin dosages by 20 – 50%, if multiple daily injections are used, using an insu-
lin pump and also decreasing the basal before exercise. These are individualistic based on blood glucose
monitoring.
Monitor glycemia before, during and after as necessary.
Taking extra carbohydrate before and hourly during exercise. This also to be individualized and based
on blood glucose monitoring.
After prolonged exercise, monitor glycemia and take extra carbohydrate to avoid delayed hypoglycemia.
Use extra caution in monitoring glycemia if exercise is being performed within 24 hrs of a hypoglycemic
episode.
Specific considerations for exercise in Type T2DM
Hypoglycemia is less common in T2DM during exercise then in T1DM and extra carbohydrate usually
unnecessary.
Patients on insulin or sulphonylureas may need to reduce the doses during exercise day guided by
glucose monitoring
Recommendations : Adults with diabetes should engage in 2–3 sessions/
Pre-exercise medical clearance is generally unneces- week of resistance exercise on nonconsecutive days.
sary for asymptomatic individuals prior to beginning Flexibility training and balance training are recom-
low- or moderate-intensity physical activity not ex- mended 2–3 times/week for older adults with diabe-
ceeding the demands of brisk walking or everyday tes. Yoga and tai chi may be included based on in-
living. dividual preferences to increase flexibility, muscular
Most adults with diabetes should engage in 150 min strength, and balance.
or more of moderate-to-vigorous intensity activi- Individuals with diabetes or pre diabetes are en-
ty weekly, spread over at least 3 days/week, with couraged to increase their total daily incidental (non
no more than 2 consecutive days without activity. exercise) physical activity to gain additional health
Shorter durations (minimum 75 min/week) of vigor- benefits.
ous intensity or interval training may be sufficient for
younger and more physically fit individuals. To gain more health benefits from physical activity
programs, participation in supervised training is rec-
Children and adolescents with type 1 or type 2 dia- ommended over non supervised programs. (Table 6)
betes should engage in 60 min/day or more of mod-
erate or vigorous intensity aerobic activity, with vigor-
ous, muscle-strengthening, and bone-strengthening
activities included at least 3 days/week.
Cardio Diabetes Medicine