Page 387 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 387
372 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
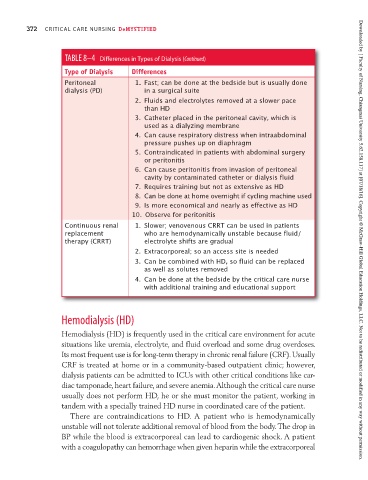
TABLE 8–4 Differences in Types of Dialysis (Continued)
Type of Dialysis Differences
Peritoneal 1. Fast; can be done at the bedside but is usually done
dialysis (PD) in a surgical suite
2. Fluids and electrolytes removed at a slower pace
than HD
3. Catheter placed in the peritoneal cavity, which is
used as a dialyzing membrane
4. Can cause respiratory distress when intraabdominal
pressure pushes up on diaphragm
5. Contraindicated in patients with abdominal surgery
or peritonitis
6. Can cause peritonitis from invasion of peritoneal
cavity by contaminated catheter or dialysis fluid
7. Requires training but not as extensive as HD
8. Can be done at home overnight if cycling machine used
9. Is more economical and nearly as effective as HD
10. Observe for peritonitis
Continuous renal 1. Slower; venovenous CRRT can be used in patients
replacement who are hemodynamically unstable because fluid/
therapy (CRRT) electrolyte shifts are gradual Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
2. Extracorporeal; so an access site is needed
3. Can be combined with HD, so fluid can be replaced
as well as solutes removed
4. Can be done at the bedside by the critical care nurse
with additional training and educational support
Hemodialysis (HD)
Hemodialysis (HD) is frequently used in the critical care environment for acute
situations like uremia, electrolyte, and fluid overload and some drug overdoses.
Its most frequent use is for long-term therapy in chronic renal failure (CRF). Usually
CRF is treated at home or in a community-based outpatient clinic; however,
dialysis patients can be admitted to ICUs with other critical conditions like car-
diac tamponade, heart failure, and severe anemia. Although the critical care nurse
usually does not perform HD, he or she must monitor the patient, working in
tandem with a specially trained HD nurse in coordinated care of the patient.
There are contraindications to HD. A patient who is hemodynamically
unstable will not tolerate additional removal of blood from the body. The drop in
BP while the blood is extracorporeal can lead to cardiogenic shock. A patient
with a coagulopathy can hemorrhage when given heparin while the extracorporeal