Page 72 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 72
30 20 ms
(see 2.15E)
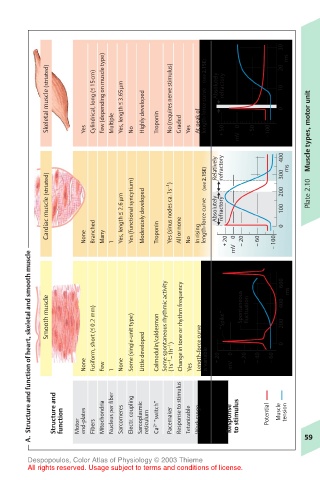
Skeletal muscle (striated) < Cylindrical, long ( – 15cm) Few (depending on muscle type) < Yes, length – 3.65µm Highly developed No (requires nerve stimulus) length-force curve Absolutely refractory 10 0
At peak of
Troponin
Multiple
Graded
Yes
+ 50
Yes
No
mV 0 – 50 –100 400 ms Muscle types, motor unit
refractory
Relatively
Cardiac muscle (striated) < Yes, length – 2.6 µm Yes (functional syncytium) Moderately developed Yes (sinus nodes ca.1s –1 ) length-force curve (see 2.15E) Absolutely refractory 300 200 100 0 Plate 2.10
All or none
Branched
Troponin
In rising
Many
None
No
1
mV + 20 0 – 20 – 60 – 100
A. Structure and function of heart, skeletal and smooth muscle
Smooth muscle < Fusiform, short ( – 0.2 mm) Some spontaneous rhythmic activity Change in tone or rhythm frequency “Spike” Spontaneous fluctuation 600 400 200 ms
None Few 1 None Some (single-unit type) Little developed Calmodulin/caldesmon (1s –1 –1h –1 ) Yes Length-force curve is variable + 20 0 mV – 20 – 40 – 60 0
Structure and function end-plates Mitochondria Nucleus per fiber Sarcomeres Electr. coupling Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ “switch” Pacemaker Response to stimulus Tetanizable Work range Response to stimulus Potential Muscle tension
Fibers
Motor
59
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.