Page 1154 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1154
CHAPTER 86: Intracranial Pressure: Monitoring and Management 793
IV pole
Height adjuster
Injection sampling port
Flow
Ventricular catheter
Three-way
m
H
mmm Hg c c cm H 2 O stopcock
2
2
0–
–0
– – – – –0 – – Zero reference
0
0–
1–
– –1 – –
–1 1 – –50– – –
– – –
2–
– –2
3–
2–
2
–2
– – – –40– – –3 – –
– –
4–
– –4
3
– – –
–3 3–
5–
–30– – –5 – –
6–
4
– – – – –6 – –
–4
4–
7–
– –7
5
–5 5– –20– – – Drip chamber Foramen of Monro
– – –
8–
– –8
– –
– – –
–6 6 6– –10– – – Drain pressure EAM
– –9
9–
– – –
–7 7 7– –10 – –
–11 – –
– – –
–8 8 8– –122 – – One-way stopcock
9–
9
– – – –13 – –
–9
–14 4 – –
– –10 0 – – –15 – –
– –11 – – –16 – – Collection bag
–17 – –
– –12 2 – – Approximmate –18 – –
– –13 3 – – Ap ppro x imat e – –
Voolume (mL) –19
2
– –14 4 – – –20 – – Pressure scales
2
7
00
– –700– – –21 – –
– –15 5 – – –22 – –
2
6
00
2
– –16 6 – – – –600– – –23 – –
–2244 – –
50
0
– –17 7 – – – –500– –
–25 – –
2
2
– –18 8 – – –400– – –26 – –
4
00
–
2
– –19 9 – – –27 – –
–300–
–300 – –28 – –
2
– –20 0 – – –29 – –
2
–200– – –30 – –
–200
3
–
–100– –
00
1
Drainage tube clamp
Drainage port
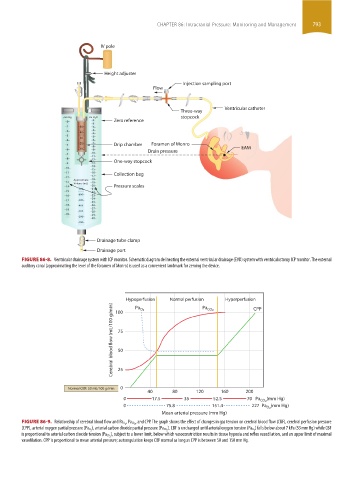
FIGURE 86-8. Ventricular drainage system with ICP monitor. Schematic diagram delineating the external ventricular drainage (EVD) system with ventriculostomy ICP monitor. The external
auditory canal (approximating the level of the foramen of Monro) is used as a convenient landmark for zeroing the device.
Hypoperfusion Normal perfusion Pa CO 2 Hyperperfusion CPP
Cerebral blood flow (mL/100 g/min) 75
Pa
O 2
100
50
0
Normal CBF: 50 mL/100 g/min 25
40 80 120 160 200
0 17.5 35 52.5 70 Pa CO 2 (mm Hg)
0 75.8 151.4 227 Pa (mm Hg)
O 2
Mean arterial pressure (mm Hg)
, and CPP. The graph shows the effect of changes in gas tension on cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral perfusion pressure
FIGURE 86-9. Relationship of cerebral blood flow and Pa O 2 , Pa CO 2
) falls below about 7 kPa (53 mm Hg) while CBF
(CPP), arterial oxygen partial pressure (Pa O 2 ), arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure (Pa CO 2 ). CBF is unchanged until arterial oxygen tension (Pa O 2
), subject to a lower limit, below which vasoconstriction results in tissue hypoxia and reflex vasodilation, and an upper limit of maximal
is proportional to arterial carbon dioxide tension (Pa CO 2
vasodilation. CPP is proportional to mean arterial pressure; autoregulation keeps CBF normal as long as CPP is between 50 and 150 mm Hg.
section06.indd 793 1/23/2015 12:55:51 PM