Page 296 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 296
200 PART 2: General Management of the Patient
A B
P
P P P
1 s 1 s PVC
RA RA
–25–
F F F F F F F F
Cannon
–0–
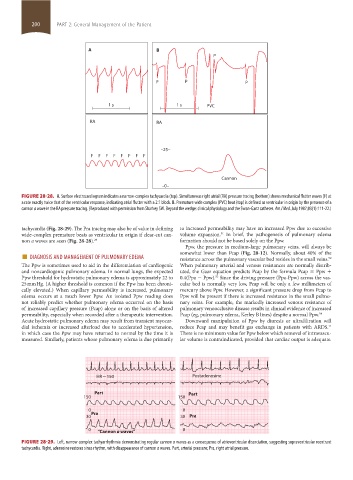
FIGURE 28-28. A. Surface electrocardiogram indicates a narrow-complex tachycardia (top). Simultaneous right atrial (RA) pressure tracing (bottom) shows mechanical flutter waves (F) at
a rate exactly twice that of the ventricular response, indicating atrial flutter with a 2:1 block. B. Premature wide complex (PVC) beat (top) is defined as ventricular in origin by the presence of a
cannon a wave in the RA pressure tracing. (Reproduced with permission from Sharkey SW. Beyond the wedge: clinical physiology and the Swan-Ganz catheter. Am J Med. July 1987;83(1):111-22.)
tachycardia (Fig. 28-29). The Pra tracing may also be of value in defining to increased permeability may have an increased Ppw due to excessive
wide-complex premature beats as ventricular in origin if clear-cut can- volume expansion. In brief, the pathogenesis of pulmonary edema
51
non a waves are seen (Fig. 28-28). 29 formation should not be based solely on the Ppw.
Ppw, the pressure in medium-large pulmonary veins, will always be
■ DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF PULMONARY EDEMA somewhat lower than Pcap (Fig. 28-12). Normally, about 40% of the
resistance across the pulmonary vascular bed resides in the small veins.
52
The Ppw is sometimes used to aid in the differentiation of cardiogenic When pulmonary arterial and venous resistances are normally distrib-
and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. In normal lungs, the expected uted, the Gaar equation predicts Pcap by the formula Pcap = Ppw +
Ppw threshold for hydrostatic pulmonary edema is approximately 22 to 0.4(Ppa − Ppw). Since the driving pressure (Ppa-Ppw) across the vas-
53
25 mm Hg. (A higher threshold is common if the Ppw has been chroni- cular bed is normally very low, Pcap will be only a few millimeters of
cally elevated.) When capillary permeability is increased, pulmonary mercury above Ppw. However, a significant pressure drop from Pcap to
edema occurs at a much lower Ppw. An isolated Ppw reading does Ppw will be present if there is increased resistance in the small pulmo-
not reliably predict whether pulmonary edema occurred on the basis nary veins. For example, the markedly increased venous resistance of
of increased capillary pressure (Pcap) alone or on the basis of altered pulmonary venoocclusive disease results in clinical evidence of increased
permeability, especially when recorded after a therapeutic intervention. Pcap (eg, pulmonary edema, Kerley B lines) despite a normal Ppw. 54
Acute hydrostatic pulmonary edema may result from transient myocar- Downward manipulation of Ppw by diuresis or ultrafiltration will
dial ischemia or increased afterload due to accelerated hypertension, reduce Pcap and may benefit gas exchange in patients with ARDS.
11
in which case the Ppw may have returned to normal by the time it is There is no minimum value for Ppw below which removal of intravascu-
measured. Similarly, patients whose pulmonary edema is due primarily lar volume is contraindicated, provided that cardiac output is adequate.
HR ~ 150 Postadenosine
Part Part
150 150
0 0
30 Pra 30 Pra
0 “Cannon a waves” 0
FIGURE 28-29. Left, narrow complex tachyarrhythmia demonstrating regular cannon a waves as a consequence of atrioventricular dissociation, suggesting supraventricular reentrant
tachycardia. Right, adenosine restores sinus rhythm, with disappearance of cannon a waves. Part, arterial pressure; Pra, right atrial pressure.
section02.indd 200 1/13/2015 2:05:43 PM