Page 98 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 98
66 PART 1: An Overview of the Approach to and Organization of Critical Care
Hospital A
Off-site command center
Audio-visual
Hospital B
EMR
Physician Staff
Hospital C
Hospital A
Hospital B
On-site command center
Audio-visual
EMR
Telemetry
Multidisciplinary Radiography
Staff
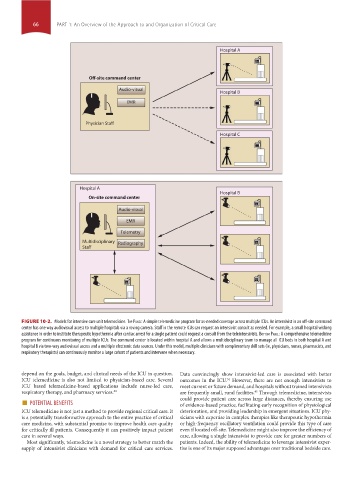
FIGURE 10-2. Models for intensive care unit telemedicine. Top panel: A simple telemedicine program for as-needed coverage across multiple ICUs. An intensivist in an off-site command
center has one way audiovisual access to multiple hospitals via a roving camera. Staff in the remote ICUs can request an intensivist consult as needed. For example, a small hospital wishing
assistance in order to institute therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest for a single patient could request a consult from the teleintensivists. BoTTom panel: A comprehensive telemedicine
program for continuous monitoring of multiple ICUs. The command center is located within hospital A and allows a multidisciplinary team to manage all ICU beds in both hospital A and
hospital B via two-way audiovisual access and a multiple electronic data sources. Under this model, multiple clinicians with complimentary skill sets (ie, physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and
respiratory therapists) can continuously monitor a large cohort of patients and intervene when necessary.
depend on the goals, budget, and clinical needs of the ICU in question. Data convincingly show intensivist-led care is associated with better
ICU telemedicine is also not limited to physician-based care. Several outcomes in the ICU. However, there are not enough intensivists to
34
ICU based telemedicine-based applications include nurse-led care, meet current or future demand, and hospitals without trained intensivists
respiratory therapy, and pharmacy services. 44 are frequently small, rural facilities. Through telemedicine, intensivists
45
■ POTENTIAL BENEFITS could provide patient care across large distances, thereby ensuring use
of evidence-based practice, facilitating early recognition of physiological
ICU telemedicine is not just a method to provide regional critical care. It deterioration, and providing leadership in emergent situations. ICU phy-
is a potentially transformative approach to the entire practice of critical sicians with expertise in complex therapies like therapeutic hypothermia
care medicine, with substantial promise to improve health care quality or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation could provide this type of care
for critically ill patients. Consequently it can positively impact patient even if located off-site. Telemedicine might also improve the efficiency of
care in several ways. care, allowing a single intensivist to provide care for greater numbers of
Most significantly, telemedicine is a novel strategy to better match the patients. Indeed, the ability of telemedicine to leverage intensivist exper-
supply of intensivist clinicians with demand for critical care services. tise is one of its major supposed advantages over traditional bedside care.
Section01.indd 66 1/22/2015 9:37:10 AM