Page 382 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 382
ECA6 7/18/06 6:54 PM Page 367
The cranial nerves 367
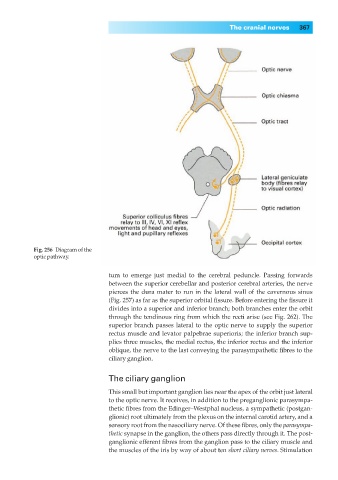
Fig. 256◊Diagram of the
optic pathway.
tum to emerge just medial to the cerebral peduncle. Passing forwards
between the superior cerebellar and posterior cerebral arteries, the nerve
pierces the dura mater to run in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus
(Fig. 257) as far as the superior orbital fissure. Before entering the fissure it
divides into a superior and inferior branch; both branches enter the orbit
through the tendinous ring from which the recti arise (see Fig. 262). The
superior branch passes lateral to the optic nerve to supply the superior
rectus muscle and levator palpebrae superioris; the inferior branch sup-
plies three muscles, the medial rectus, the inferior rectus and the inferior
oblique, the nerve to the last conveying the parasympathetic fibres to the
ciliary ganglion.
The ciliary ganglion
This small but important ganglion lies near the apex of the orbit just lateral
to the optic nerve. It receives, in addition to the preganglionic parasympa-
thetic fibres from the Edinger–Westphal nucleus, a sympathetic (postgan-
glionic) root ultimately from the plexus on the internal carotid artery, and a
sensory root from the nasociliary nerve. Of these fibres, only the parasympa-
thetic synapse in the ganglion, the others pass directly through it. The post-
ganglionic efferent fibres from the ganglion pass to the ciliary muscle and
the muscles of the iris by way of about ten short ciliary nerves. Stimulation