Page 409 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 409
ECA6 7/18/06 6:54 PM Page 394
394 The central nervous system
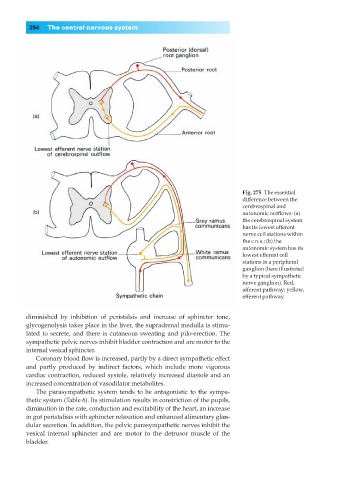
Fig. 275◊The essential
difference between the
cerebrospinal and
autonomic outflows: (a)
the cerebrospinal system
has its lowest efferent
nerve cell stations within
the c.n.s.; (b) the
autonomic system has its
lowest efferent cell
stations in a peripheral
ganglion (here illustrated
by a typical sympathetic
nerve ganglion). Red,
afferent pathway; yellow,
efferent pathway.
diminished by inhibition of peristalsis and increase of sphincter tone,
glycogenolysis takes place in the liver, the supradrenal medulla is stimu-
lated to secrete, and there is cutaneous sweating and pilo-erection. The
sympathetic pelvic nerves inhibit bladder contraction and are motor to the
internal vesical sphincter.
Coronary blood flow is increased, partly by a direct sympathetic effect
and partly produced by indirect factors, which include more vigorous
cardiac contraction, reduced systole, relatively increased diastole and an
increased concentration of vasodilator metabolites.
The parasympathetic system tends to be antagonistic to the sympa-
thetic system (Table 6). Its stimulation results in constriction of the pupils,
diminution in the rate, conduction and excitability of the heart, an increase
in gut peristalisis with sphincter relaxation and enhanced alimentary glan-
dular secretion. In addition, the pelvic parasympathetic nerves inhibit the
vesical internal sphincter and are motor to the detrusor muscle of the
bladder.