Page 410 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 410
ECA6 7/18/06 6:54 PM Page 395
The autonomic nervous system 395
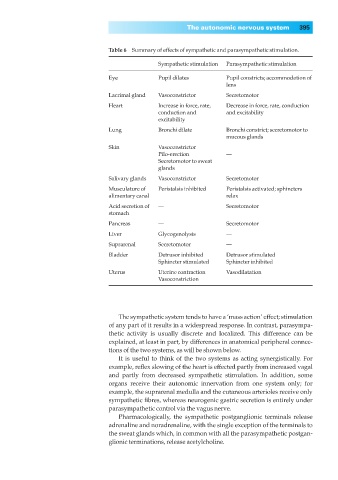
Table 6◊◊Summary of effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation.
Sympathetic stimulation Parasympathetic stimulation
Eye Pupil dilates Pupil constricts; accommodation of
lens
Lacrimal gland Vasoconstrictor Secretomotor
Heart Increase in force, rate, Decrease in force, rate, conduction
conduction and and excitability
excitability
Lung Bronchi dilate Bronchi constrict; secretomotor to
mucous glands
Skin Vasoconstrictor
Pilo-erection —
Secretomotor to sweat
glands
Salivary glands Vasoconstrictor Secretomotor
Musculature of Peristalsis inhibited Peristalsis activated; sphincters
alimentary canal relax
Acid secretion of — Secretomotor
stomach
Pancreas — Secretomotor
Liver Glycogenolysis —
Suprarenal Secretomotor —
Bladder Detrusor inhibited Detrusor stimulated
Sphincter stimulated Sphincter inhibited
Uterus Uterine contraction Vasodilatation
Vasoconstriction
The sympathetic system tends to have a ‘mass action’ effect; stimulation
of any part of it results in a widespread response. In contrast, parasympa-
thetic activity is usually discrete and localized. This difference can be
explained, at least in part, by differences in anatomical peripheral connec-
tions of the two systems, as will be shown below.
It is useful to think of the two systems as acting synergistically. For
example, reflex slowing of the heart is effected partly from increased vagal
and partly from decreased sympathetic stimulation. In addition, some
organs receive their autonomic innervation from one system only; for
example, the suprarenal medulla and the cutaneous arterioles receive only
sympathetic fibres, whereas neurogenic gastric secretion is entirely under
parasympathetic control via the vagus nerve.
Pharmacologically, the sympathetic postganglionic terminals release
adrenaline and noradrenaline, with the single exception of the terminals to
the sweat glands which, in common with all the parasympathetic postgan-
glionic terminations, release acetylcholine.