Page 84 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 84
ECA2 7/18/06 6:42 PM Page 69
Peritoneal cavity 69
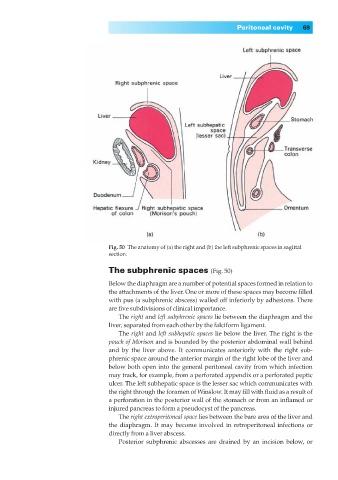
Fig. 50◊The anatomy of (a) the right and (b) the left subphrenic spaces in sagittal
section.
The subphrenic spaces (Fig. 50)
Below the diaphragm are a number of potential spaces formed in relation to
the attachments of the liver. One or more of these spaces may become filled
with pus (a subphrenic abscess) walled off inferiorly by adhesions. There
are five subdivisions of clinical importance.
The right and left subphrenic spaces lie between the diaphragm and the
liver, separated from each other by the falciform ligament.
The right and left subhepatic spaces lie below the liver. The right is the
pouch of Morison and is bounded by the posterior abdominal wall behind
and by the liver above. It communicates anteriorly with the right sub-
phrenic space around the anterior margin of the right lobe of the liver and
below both open into the general peritoneal cavity from which infection
may track, for example, from a perforated appendix or a perforated peptic
ulcer. The left subhepatic space is the lesser sac which communicates with
the right through the foramen of Winslow. It may fill with fluid as a result of
a perforation in the posterior wall of the stomach or from an inflamed or
injured pancreas to form a pseudocyst of the pancreas.
The right extraperitoneal space lies between the bare area of the liver and
the diaphragm. It may become involved in retroperitoneal infections or
directly from a liver abscess.
Posterior subphrenic abscesses are drained by an incision below, or