Page 22 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 22
Plate 1-7 Integumentary System
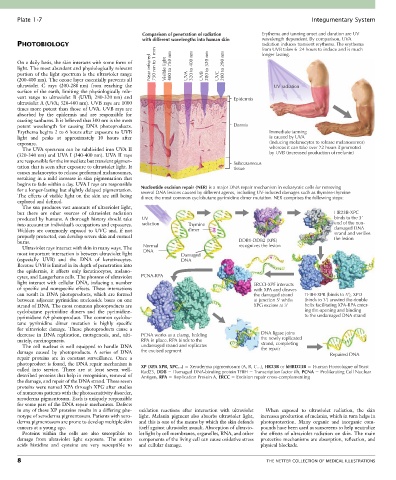
Comparison of penetration of radiation Erythema and tanning onset and duration are UV
with different wavelengths into human skin wavelength dependent. By comparison, UVA
PHOTOBIOLOGY radiation induces transient erythema. The erythema
from UVB takes 6–24 hours to induce and is much
On a daily basis, the skin interacts with some form of 750 nm to 1 mm longer lasting.
light. The most abundant and physiologically relevant Near infrared Visible light 400 to 750 nm 320 to 400 nm 280 to 320 nm 200 to 290 nm
portion of the light spectrum is the ultraviolet range UVA UVB UVC
(200-400 nm). The ozone layer essentially prevents all
ultraviolet C rays (200-280 nm) from reaching the UV radiation
surface of the earth, limiting the physiologically rele-
vant range to ultraviolet B (UVB; 280-320 nm) and Epidermis
ultraviolet A (UVA; 320-400 nm). UVB rays are 1000
times more potent than those of UVA. UVB rays are
absorbed by the epidermis and are responsible for
causing sunburns. It is believed that 300 nm is the most
potent wavelength for causing DNA photoproducts. Dermis
Erythema begins 2 to 6 hours after exposure to UVB Immediate tanning
light and peaks at approximately 10 hours after is caused by UVA
exposure. (inducing melanocytes to release melanosomes)
The UVA spectrum can be subdivided into UVA II whereas it can take over 72 hours if promoted
(320-340 nm) and UVA I (340-400 nm). UVA II rays by UVB (increased production of melanin)
are responsible for the immediate but transient pigmen- Subcutaneous
tation that is seen after exposure to ultraviolet light. It tissue
causes melanocytes to release preformed melanosomes,
resulting in a mild increase in skin pigmentation that
begins to fade within a day. UVA I rays are responsible
for a longer-lasting but slightly delayed pigmentation. Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is a major DNA repair mechanism in eukaryotic cells for removing
several DNA lesions caused by different agents, including UV-induced damages such as thymine-thymine
The effects of visible light on the skin are still being dimer, the most common cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer mutation. NER comprises the following steps:
explored and defined.
The sun produces vast amounts of ultraviolet light,
but there are other sources of ultraviolet radiation HR23B-XPC
produced by humans. A thorough history should take UV binds to the 3’
into account an individual’s occupations and exposures. radiation Thymine end of the non-
Welders are commonly exposed to UVC and, if not dimer damaged DNA
properly protected, can develop severe skin and corneal strand and verifies
the lesion
burns. DDB1-DDB2 (XPE)
Ultraviolet rays interact with skin in many ways. The Normal recognizes the lesion
most important interaction is between ultraviolet light DNA Damaged
(especially UVB) and the DNA of keratinocytes. DNA
Because UVB is limited in its depth of penetration into
the epidermis, it affects only keratinocytes, melano-
cytes, and Langerhans cells. The photons of ultraviolet PCNA-RPA
light interact with cellular DNA, inducing a number ERCCI-XPF interacts
of specific and nonspecific effects. These interactions with XPA and cleaves
can result in DNA photoproducts, which are formed the damaged strand TFIIH-XPB (binds to 5’), XPD
between adjacent pyrimidine nucleoside bases on one at junction 5’ while (binds to 3’) unwind the double
strand of DNA. The most common photoproducts are XPG excises at 3’ helix facilitating XPA-RPA enter-
cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and the pyrimidine- ing the opening and binding
pyrimidone 6,4 photoproduct. The common cyclobu- to the undamaged DNA strand
tane pyrimidine dimer mutation is highly specific
for ultraviolet damage. These photoproducts cause a
decrease in DNA replication, mutagenesis, and, ulti- PCNA works as a clamp, holding DNA ligase joins
mately, carcinogenesis. RPA in place. RPA binds to the the newly replicated
The cell nucleus is well equipped to handle DNA undamaged strand and replicates strand, completing
damage caused by photoproducts. A series of DNA the excised segment the repair Repaired DNA
repair proteins are in constant surveillance. Once a
photoproduct is found, the DNA repair mechanism is
called into service. There are at least seven well- XP (XPA XPB, XPC...) Xeroderma pigmentosum (A, B, C...), HR23B or hHRD23B Human Homologue of Yeast
Rad23, DDB Damaged DNA-binding protein TFIIH Transcription factor iih, PCNA Proliferating Cell Nuclear
described proteins that help in recognition, removal of Antigen, RPA Replication Protein A, ERCC Excision repair cross-complementing
the damage, and repair of the DNA strand. These seven
proteins were named XPA through XPG after studies
of numerous patients with the photosensitivity disorder,
xeroderma pigmentosum. Each is uniquely responsible
for some part of the DNA repair mechanism. Defects
in any of these XP proteins results in a differing phe- oxidation reactions after interaction with ultraviolet When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, the skin
notype of xeroderma pigmentosum. Patients with xero- light. Melanin pigment also absorbs ultraviolet light, increases production of melanin, which in turn helps in
derma pigmentosum are prone to develop multiple skin and this is one of the means by which the skin defends photoprotection. Many organic and inorganic com-
cancers at a young age. itself against ultraviolet assault. Absorption of ultravio- pounds have been used as sunscreens to help neutralize
Proteins within the cells are also susceptible to let light by cell membranes, organelles, RNA, and other the effects of ultraviolet radiation on skin. The main
damage from ultraviolet light exposure. The amino components of the living cell can cause oxidative stress protective mechanisms are absorption, reflection, and
acids histidine and cysteine are very susceptible to and cellular damage. physical blockade.
8 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS