Page 144 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 144
110 Chapter 4
40 A B
35
Airway Pressure (cm H 2 O) 25
30
20
15
10
© Cengage Learning 2014
5
0
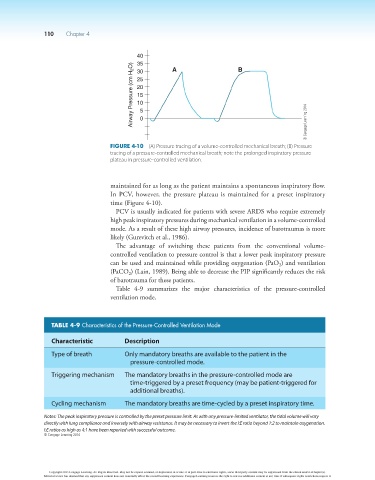
Figure 4-10 (A) Pressure tracing of a volume-controlled mechanical breath; (B) Pressure
tracing of a pressure-controlled mechanical breath; note the prolonged inspiratory pressure
plateau in pressure-controlled ventilation.
maintained for as long as the patient maintains a spontaneous inspiratory flow.
In PCV, however, the pressure plateau is maintained for a preset inspiratory
time (Figure 4-10).
PCV is usually indicated for patients with severe ARDS who require extremely
high peak inspiratory pressures during mechanical ventilation in a volume-controlled
mode. As a result of these high airway pressures, incidence of barotraumas is more
likely (Gurevitch et al., 1986).
The advantage of switching these patients from the conventional volume-
controlled ventilation to pressure control is that a lower peak inspiratory pressure
can be used and maintained while providing oxygenation (PaO ) and ventilation
2
(PaCO ) (Lain, 1989). Being able to decrease the PIP significantly reduces the risk
2
of barotrauma for these patients.
Table 4-9 summarizes the major characteristics of the pressure-controlled
ventilation mode.
TABLE 4-9 Characteristics of the Pressure-Controlled Ventilation Mode
Characteristic Description
Type of breath Only mandatory breaths are available to the patient in the
pressure-controlled mode.
Triggering mechanism The mandatory breaths in the pressure-controlled mode are
time-triggered by a preset frequency (may be patient-triggered for
additional breaths).
Cycling mechanism The mandatory breaths are time-cycled by a preset inspiratory time.
Notes: The peak inspiratory pressure is controlled by the preset pressure limit. As with any pressure-limited ventilator, the tidal volume will vary
directly with lung compliance and inversely with airway resistance. It may be necessary to invert the I:E ratio beyond 1:2 to maintain oxygenation.
I:E ratios as high as 4:1 have been reported with successful outcome.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.