Page 422 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 422
388 Chapter 12
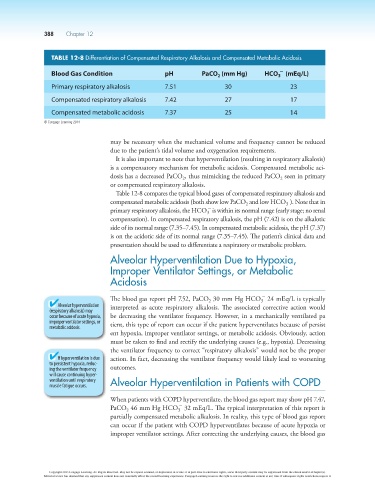
TABLE 12-8 Differentiation of Compensated Respiratory Alkalosis and Compensated Metabolic Acidosis
2
Blood Gas Condition pH PaCO (mm Hg) HCO (mEq/L)
2
3
Primary respiratory alkalosis 7.51 30 23
Compensated respiratory alkalosis 7.42 27 17
Compensated metabolic acidosis 7.37 25 14
© Cengage Learning 2014
may be necessary when the mechanical volume and frequency cannot be reduced
due to the patient’s tidal volume and oxygenation requirements.
It is also important to note that hyperventilation (resulting in respiratory alkalosis)
is a compensatory mechanism for metabolic acidosis. Compensated metabolic aci-
dosis has a decreased PaCO , thus mimicking the reduced PaCO seen in primary
2
2
or compensated respiratory alkalosis.
Table 12-8 compares the typical blood gases of compensated respiratory alkalosis and
-
compensated metabolic acidosis (both show low PaCO and low HCO ). Note that in
2
3
-
primary respiratory alkalosis, the HCO is within its normal range (early stage; no renal
3
compensation). In compensated respiratory alkalosis, the pH (7.42) is on the alkalotic
side of its normal range (7.35–7.45). In compensated metabolic acidosis, the pH (7.37)
is on the acidotic side of its normal range (7.35–7.45). The patient’s clinical data and
presentation should be used to differentiate a respiratory or metabolic problem.
Alveolar Hyperventilation Due to Hypoxia,
Improper Ventilator Settings, or Metabolic
Acidosis
-
The blood gas report pH 7.52, PaCO 30 mm Hg HCO 24 mEq/L is typically
3
2
Alveolar hyperventilation interpreted as acute respiratory alkalosis. The associated corrective action would
(respiratory alkalosis) may
occur because of acute hypoxia, be decreasing the ventilator frequency. However, in a mechanically ventilated pa
improper ventilator settings, or tient, this type of report can occur if the patient hyperventilates because of persist
metabolic acidosis.
ent hypoxia, improper ventilator settings, or metabolic acidosis. Obviously, action
must be taken to find and rectify the underlying causes (e.g., hypoxia). Decreasing
the ventilator frequency to correct “respiratory alkalosis” would not be the proper
If hyperventilation is due action. In fact, decreasing the ventilator frequency would likely lead to worsening
to persistent hypoxia, reduc-
ing the ventilator frequency outcomes.
will cause continuing hyper-
ventilation until respiratory Alveolar Hyperventilation in Patients with COPD
muscle fatigue occurs.
When patients with COPD hyperventilate, the blood gas report may show pH 7.47,
-
PaCO 46 mm Hg HCO 32 mEq/L. The typical interpretation of this report is
2
3
partially compensated metabolic alkalosis. In reality, this type of blood gas report
can occur if the patient with COPD hyperventilates because of acute hypoxia or
improper ventilator settings. After correcting the underlying causes, the blood gas
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.