Page 42 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 42
8 Chapter 1
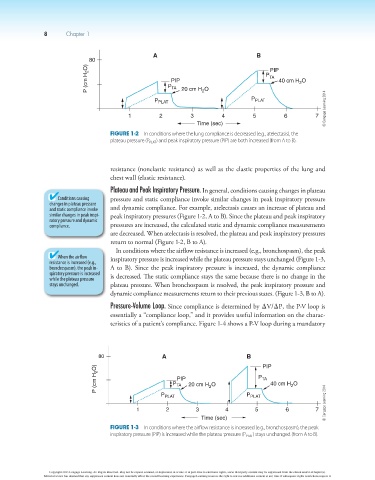
A B
80
P (cm H 2 O) P PIP 20 cm H O P TA 40 cm H O
PIP
2
TA
2
P
P PLAT PLAT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 © Cengage Learning 2014
Time (sec)
Figure 1-2 In conditions where the lung compliance is decreased (e.g., atelectasis), the
plateau pressure (P PLAT ) and peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) are both increased (from A to B).
resistance (nonelastic resistance) as well as the elastic properties of the lung and
chest wall (elastic resistance).
Plateau and Peak Inspiratory Pressure. In general, conditions causing changes in plateau
Conditions causing pressure and static compliance invoke similar changes in peak inspiratory pressure
changes in plateau pressure
and static compliance invoke and dynamic compliance. For example, atelectasis causes an increase of plateau and
similar changes in peak inspi- peak inspiratory pressures (Figure 1-2, A to B). Since the plateau and peak inspiratory
ratory pressure and dynamic
compliance. pressures are increased, the calculated static and dynamic compliance measurements
are decreased. When atelectasis is resolved, the plateau and peak inspiratory pressures
return to normal (Figure 1-2, B to A).
In conditions where the airflow resistance is increased (e.g., bronchospasm), the peak
When the airflow inspiratory pressure is increased while the plateau pressure stays unchanged (Figure 1-3,
resistance is increased (e.g.,
bronchospasm), the peak in- A to B). Since the peak inspiratory pressure is increased, the dynamic compliance
spiratory pressure is increased is decreased. The static compliance stays the same because there is no change in the
while the plateau pressure
stays unchanged. plateau pressure. When bronchospasm is resolved, the peak inspiratory pressure and
dynamic compliance measurements return to their previous states. (Figure 1-3, B to A).
Pressure-Volume Loop. Since compliance is determined by DV/DP, the P-V loop is
essentially a “compliance loop,” and it provides useful information on the charac-
teristics of a patient’s compliance. Figure 1-4 shows a P-V loop during a mandatory
80 A B PIP
P (cm H 2 O) P TA 20 cm H O P TA 40 cm H O
PIP
2
2
P PLAT P PLAT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 © Cengage Learning 2014
Time (sec)
Figure 1-3 In conditions where the airflow resistance is increased (e.g., bronchospasm), the peak
inspiratory pressure (PIP) is increased while the plateau pressure (P PLAT ) stays unchanged (from A to B).
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.