Page 424 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 424
390 Chapter 12
all likelihood, the low volume alarm will also be triggered since pressure and volume
The low pressure are affected simultaneously by similar clinical conditions.
alarm may be triggered in
(1) loss of circuit pressure Conditions that may trigger the low pressure alarm may be grouped into four
(a common event), (2) loss of
system pressure (an uncommon areas: (1) loss of circuit pressure (a common event), (2) loss of system pressure
occurrence), (3) conditions lead- (an uncommon occurrence), (3) conditions leading to premature termination of
ing to premature termination
of inspiratory phase, and (4) inspiratory phase, and (4) inappropriate ventilator settings. These conditions and
inappropriate ventilator settings. selected examples are listed in Table 12-9.
Low Expired Volume Alarm
The low volume limit is set to ensure that the patient receives (and exhales) a
minimum volume.
The low expired volume alarm is triggered when the expired volume drops
below the preset low volume limit. If the preset low expired volume limit is set at
400 mL, and the expired volume drops below 400 mL, the low volume alarm will
The low volume alarm be triggered.
is usually triggered along
with the low pressure alarm As mentioned before, the low volume alarm is usually triggered along with
because loss of airway pres- the low pressure alarm because loss of airway pressure usually results in loss of
sure usually results in loss of
volume delivered. volume. See Table 12-9 for examples of conditions that may trigger low volume
alarm.
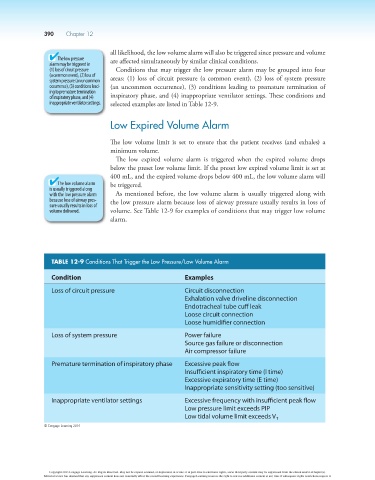
TABLE 12-9 Conditions That Trigger the Low Pressure/Low Volume Alarm
Condition Examples
Loss of circuit pressure Circuit disconnection
Exhalation valve driveline disconnection
Endotracheal tube cuff leak
Loose circuit connection
Loose humidifier connection
Loss of system pressure Power failure
Source gas failure or disconnection
Air compressor failure
Premature termination of inspiratory phase Excessive peak flow
Insufficient inspiratory time (I time)
Excessive expiratory time (E time)
Inappropriate sensitivity setting (too sensitive)
Inappropriate ventilator settings Excessive frequency with insufficient peak flow
Low pressure limit exceeds PIP
Low tidal volume limit exceeds V T
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.