Page 425 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 425
Management of Mechanical Ventilation 391
High Pressure Alarm
The high pressure limit is set to control the maximum ventilator circuit pressure
during a complete breathing cycle, usually during the inspiratory phase.
The high pressure alarm is triggered when the circuit pressure reaches or exceeds the
The high pressure preset high pressure limit. If the high pressure limit is set at 60 cm H O, and the cir-
alarm may be triggered in 2
the following conditions: cuit pressure reaches or exceeds 60 cm H O, the high pressure alarm will be triggered.
2
(1) increase in airflow resis- Conditions that trigger the high pressure alarm may be (1) increase in airflow
tance and (2) decrease in lung
or chest wall compliance. resistance and (2) decrease in lung or chest wall compliance. These conditions and
examples are shown in Table 12-10.
High Frequency Alarm
The high frequency limit is set to alert the practitioner that the patient has experi-
enced tachypnea.
The high frequency alarm
may be triggered due to (1) This alarm is triggered when the total frequency exceeds the high frequency limit.
the patient’s need to increase Autotriggering of mechanical breaths can trigger the high frequency alarm due to in-
ventilation and (2) an exces-
sive sensitivity setting. creasing inspiratory effort or incorrect sensitivity setting. Triggering of the high fre-
quency alarm often indicates that the patient is becoming tachypneic-a sign of respiratory
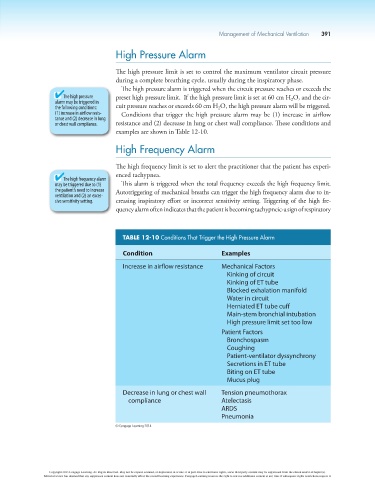
TABLE 12-10 Conditions That Trigger the High Pressure Alarm
Condition Examples
Increase in airflow resistance Mechanical Factors
Kinking of circuit
Kinking of ET tube
Blocked exhalation manifold
Water in circuit
Herniated ET tube cuff
Main-stem bronchial intubation
High pressure limit set too low
Patient Factors
Bronchospasm
Coughing
Patient-ventilator dyssynchrony
Secretions in ET tube
Biting on ET tube
Mucus plug
Decrease in lung or chest wall Tension pneumothorax
compliance Atelectasis
ARDS
Pneumonia
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.