Page 472 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 472
438 Chapter 13
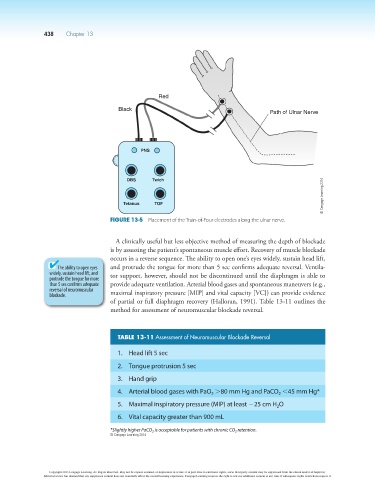
Red
Black
Path of Ulnar Nerve
PNS
DBS Twich
© Cengage Learning 2014
Tetanus TOF
Figure 13-5 Placement of the Train-of-Four electrodes along the ulnar nerve.
A clinically useful but less objective method of measuring the depth of blockade
is by assessing the patient’s spontaneous muscle effort. Recovery of muscle blockade
occurs in a reverse sequence. The ability to open one’s eyes widely, sustain head lift,
The ability to open eyes and protrude the tongue for more than 5 sec confirms adequate reversal. Ventila-
widely, sustain head lift, and tor support, however, should not be discontinued until the diaphragm is able to
protrude the tongue for more
than 5 sec confirms adequate provide adequate ventilation. Arterial blood gases and spontaneous maneuvers (e.g.,
reversal of neuromuscular
blockade. maximal inspiratory pressure [MIP] and vital capacity [VC]) can provide evidence
of partial or full diaphragm recovery (Halloran, 1991). Table 13-11 outlines the
method for assessment of neuromuscular blockade reversal.
TABLE 13-11 Assessment of Neuromuscular Blockade Reversal
1. Head lift 5 sec
2. Tongue protrusion 5 sec
3. Hand grip
4. Arterial blood gases with PaO .80 mm Hg and PaCO ,45 mm Hg*
2
2
5. Maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) at least 225 cm H O
2
6. Vital capacity greater than 900 mL
*Slightly higher PaCO 2 is acceptable for patients with chronic CO 2 retention.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.