Page 473 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 473
Pharmacotherapy for Mechanical Ventilation 439
CENTRAL NERVOUS SySTEM AGENTS
Medications that act on the central nervous system are often categorized by
their primary effect, but this can create problems when the substance has mul-
tiple effects (which is the case for many). It is less confusing to categorize a drug
by its composition rather than by one of its therapeutic effects. For instance, a
benzodiazepine can produce sedation to the point of sleep (hypnotic sedative),
anxiety relief (anxiolytic), amnesia, muscle relaxation, and relief from seizures.
Ketamine is an unusual drug in that it has both analgesic and sedation prop-
erties. Common terms for central nervous system effects include anesthesia
(diminished bodily sensation), analgesia (relief of pain), sedation (diminished
awareness or consciousness), and neurolepsis (a particular alteration of con-
sciousness that produces reduced anxiety, calming, and indifference to one’s
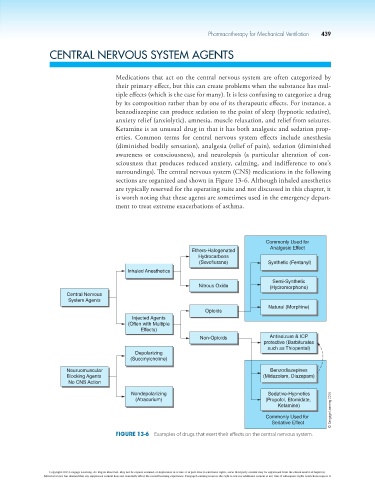
surroundings). The central nervous system (CNS) medications in the following
sections are organized and shown in Figure 13-6. Although inhaled anesthetics
are typically reserved for the operating suite and not discussed in this chapter, it
is worth noting that these agents are sometimes used in the emergency depart-
ment to treat extreme exacerbations of asthma.
Commonly Used for
Analgesic Effect
Ethers-Halogenated
Hydrocarbons
(Sevoflurane) Synthetic (Fentanyl)
Inhaled Anesthetics
Semi-Synthetic
Nitrous Oxide (Hydromorphone)
Central Nervous
System Agents
Natural (Morphine)
Opioids
Injected Agents
(Often with Multiple
Effects)
Non-Opioids Antiseizure & ICP
protective (Barbiturates
such as Thiopental)
Depolarizing
(Succinylcholine)
Neuruomuscular Benzodiazepines
Blocking Agents (Midazolam, Diazepam)
No CNS Action
Nondepolarizing Sedative-Hypnotics
(Atracurium) (Propofol, Etomidate,
Ketamine) © Cengage Learning 2014
Commonly Used for
Sedative Effect
Figure 13-6 Examples of drugs that exert their effects on the central nervous system.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.