Page 55 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 55
Principles of Mechanical Ventilation 21
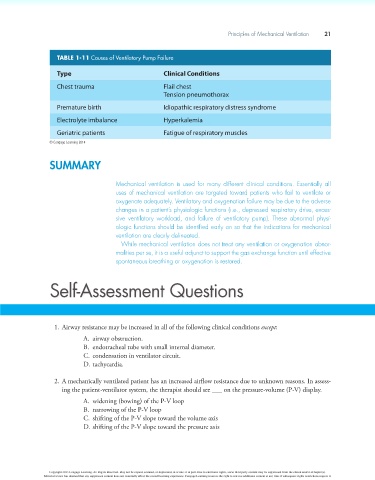
TABLE 1-11 Causes of Ventilatory Pump Failure
Type Clinical Conditions
Chest trauma Flail chest
Tension pneumothorax
Premature birth Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome
Electrolyte imbalance Hyperkalemia
Geriatric patients Fatigue of respiratory muscles
© Cengage Learning 2014
SUMMARY
Mechanical ventilation is used for many different clinical conditions. Essentially all
uses of mechanical ventilation are targeted toward patients who fail to ventilate or
oxygenate adequately. Ventilatory and oxygenation failure may be due to the adverse
changes in a patient’s physiologic functions (i.e., depressed respiratory drive, exces-
sive ventilatory workload, and failure of ventilatory pump). These abnormal physi-
ologic functions should be identified early on so that the indications for mechanical
ventilation are clearly delineated.
While mechanical ventilation does not treat any ventilation or oxygenation abnor-
malities per se, it is a useful adjunct to support the gas exchange function until effective
spontaneous breathing or oxygenation is restored.
Self-Assessment Questions
1. Airway resistance may be increased in all of the following clinical conditions except:
A. airway obstruction.
B. endotracheal tube with small internal diameter.
C. condensation in ventilator circuit.
D. tachycardia.
2. A mechanically ventilated patient has an increased airflow resistance due to unknown reasons. In assess-
ing the patient-ventilator system, the therapist should see ___ on the pressure-volume (P-V) display.
A. widening (bowing) of the P-V loop
B. narrowing of the P-V loop
C. shifting of the P-V slope toward the volume axis
D. shifting of the P-V slope toward the pressure axis
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.