Page 57 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 57
Principles of Mechanical Ventilation 23
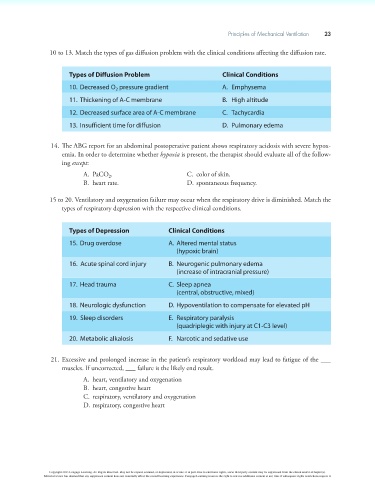
10 to 13. Match the types of gas diffusion problem with the clinical conditions affecting the diffusion rate.
Types of Diffusion Problem Clinical Conditions
10. Decreased O pressure gradient A. Emphysema
2
11. Thickening of A-C membrane B. High altitude
12. Decreased surface area of A-C membrane C. Tachycardia
13. Insufficient time for diffusion D. Pulmonary edema
14. The ABG report for an abdominal postoperative patient shows respiratory acidosis with severe hypox-
emia. In order to determine whether hypoxia is present, the therapist should evaluate all of the follow-
ing except:
A. PaCO . C. color of skin.
2
B. heart rate. D. spontaneous frequency.
15 to 20. Ventilatory and oxygenation failure may occur when the respiratory drive is diminished. Match the
types of respiratory depression with the respective clinical conditions.
Types of Depression Clinical Conditions
15. Drug overdose A. Altered mental status
(hypoxic brain)
16. Acute spinal cord injury B. Neurogenic pulmonary edema
(increase of intracranial pressure)
17. Head trauma C. Sleep apnea
(central, obstructive, mixed)
18. Neurologic dysfunction D. Hypoventilation to compensate for elevated pH
19. Sleep disorders E. Respiratory paralysis
(quadriplegic with injury at C1-C3 level)
20. Metabolic alkalosis F. Narcotic and sedative use
21. Excessive and prolonged increase in the patient’s respiratory workload may lead to fatigue of the ___
muscles. If uncorrected, ___ failure is the likely end result.
A. heart, ventilatory and oxygenation
B. heart, congestive heart
C. respiratory, ventilatory and oxygenation
D. respiratory, congestive heart
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.