Page 53 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 53
Principles of Mechanical Ventilation 19
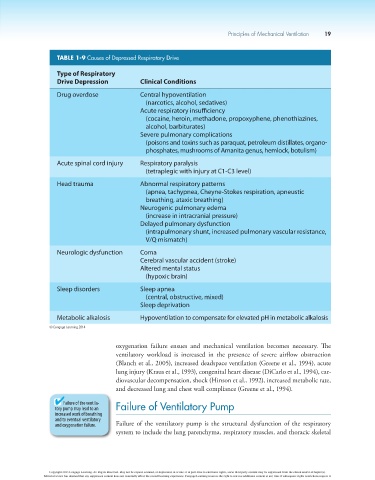
TABLE 1-9 Causes of Depressed Respiratory Drive
Type of Respiratory
Drive Depression Clinical Conditions
Drug overdose Central hypoventilation
(narcotics, alcohol, sedatives)
Acute respiratory insufficiency
(cocaine, heroin, methadone, propoxyphene, phenothiazines,
alcohol, barbiturates)
Severe pulmonary complications
(poisons and toxins such as paraquat, petroleum distillates, organo-
phosphates, mushrooms of Amanita genus, hemlock, botulism)
Acute spinal cord injury Respiratory paralysis
(tetraplegic with injury at C1-C3 level)
Head trauma Abnormal respiratory patterns
(apnea, tachypnea, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, apneustic
breathing, ataxic breathing)
Neurogenic pulmonary edema
(increase in intracranial pressure)
Delayed pulmonary dysfunction
(intrapulmonary shunt, increased pulmonary vascular resistance,
V/Q mismatch)
Neurologic dysfunction Coma
Cerebral vascular accident (stroke)
Altered mental status
(hypoxic brain)
Sleep disorders Sleep apnea
(central, obstructive, mixed)
Sleep deprivation
Metabolic alkalosis Hypoventilation to compensate for elevated pH in metabolic alkalosis
© Cengage Learning 2014
oxygenation failure ensues and mechanical ventilation becomes necessary. The
ventilatory workload is increased in the presence of severe airflow obstruction
(Blanch et al., 2005), increased deadspace ventilation (Greene et al., 1994), acute
lung injury (Kraus et al., 1993), congenital heart disease (DiCarlo et al., 1994), car-
diovascular decompensation, shock (Hinson et al., 1992), increased metabolic rate,
and decreased lung and chest wall compliance (Greene et al., 1994).
Failure of the ventila- Failure of Ventilatory Pump
tory pump may lead to an
increased work of breathing
and to eventual ventilatory
and oxygenation failure. Failure of the ventilatory pump is the structural dysfunction of the respiratory
system to include the lung parenchyma, respiratory muscles, and thoracic skeletal
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.