Page 671 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 671
2:0
2:0
1
1
1
1 A
Pa
Pa
M
1 A
M
/09
xd
xd
q
q
q
6
/09
/09
/30
6
/30
Pa
ara
ara
t
p
t
a
c.
c.
In
a
In
p
e 6
e 6
g
g
g
47
A
p
A
47
47
p
p
27_
27_
8-6
8-6
63
63
54.
LWB
LWBK340-c27_
LWB K34 0-c 27_ pp638-654.qxd 6/30/09 12:01 AM Page 647 Aptara Inc.
54.
54.
0-c
K34
C HAPTER 2 7 / Sudden Cardiac Death and Cardiac Arrest 647
1
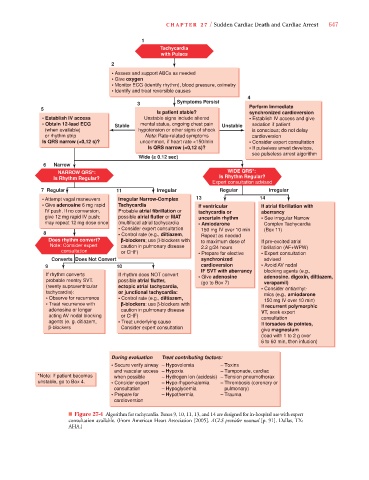
Tachycardia
with Pulses
2
• Assess and support ABCs as needed
• Give oxygen
• Monitor ECG (identify rhythm), blood pressure, oximetry
• Identify and treat reversible causes
4
3 Symptoms Persist
5 Perform Immediate
Is patient stable? synchronized cardioversion
• Establish IV access Unstable signs include altered • Establish IV access and give
• Obtain 12-lead ECG Stable mental status, ongoing chest pain Unstable sedation if patient
(when available) hypotension or other signs of shock is conscious; do not delay
or rhythm strip Note: Rate-related symptoms cardioversion
Is QRS narrow (<0,12 s)? uncommon, if heart rate <150/min • Consider expert consultation
Is QRS narrow (<0,12 s)? • If pulseless arrest develops,
see pulseless arrest algorithm
Wide (> 0.12 sec)
6 Narrow
NARROW QRS*: WIDE QRS*:
Is Rhythm Regular? Is Rhythm Regular?
Expert consultation advised
7 Regular 11 Irregular Regular Irregular
• Attempt vagal maneuvers Irregular Narrow-Complex 13 14
• Give adenosine 6 mg rapid Tachycardia If ventricular If atrial fibrillation with
IV push. If no conversion, Probable atrial fibrillation or tachycardia or aberrancy
give 12 mg rapid IV push; possible alrial flutler or MAT uncertain rhythm • See irregular Narrow
may repeat 12 mg dose once (multifocal atrial tachycardia • Amiodarone Complex Tachycardia
• Consider expert consultation 150 mg IV over 10 min (Box 11)
8 • Control rate (e.g., diltiazem, Repeat as needed
Does rhythm convert? -blockers; use β-blockers with to maximum dose of If pre-excited atrial
Note: Consider expert caution in pulmonary disease 2.2 g/24 hours fibrillation (AF+WPW)
consultation or CHF) • Prepare for elective • Expert consultation
Converts Does Not Convert synchronized advised
9 10 cardioversion • Avoid AV nodal
IF SVT with aberrancy blocking agents (e.g.,
If rhythm converts If rhythm does NOT convert • Give adenosine adenosine. digoxin, diltiazem,
probable reentry SVT. possible atrial flutter, (go to Box 7) verapamil)
(reenty supraventricular ectopic atrial tachycardia, • Consider antiarrhyt-
tachycardia): or junctional tachycardia: mics (e.g., amiodarone
• Observe for recurrence • Control rate (e.g., diltiazem, 150 mg IV over 10 min)
• Treat recurrence with -blockers: use β-blockers with If recurrent polymorphic
adenosine or longer caution in pulmonary disease VT, seek expert
acting AV nodal blocking or CHF) consultation
agents (e. g. ditiazem, • Treat underlying cause If torsades de pointes,
β-blockers Consider expert consultation
give magnesium
(load with 1 to 2 g over
6 to 60 min, then infusion)
During evaluation Treat contributing factors:
• Secure verify airway – Hypovolemia – Toxins
and vascular access – Hypoxia – Tamponade, cardiac
*Note: If patient becomes when possible – Hydrogen lon (acidosis) – Tension pneumothorax
unstable, go to Box 4. • Consider expert – Hypo-/hyperkalemia – Thrombosis (coronary or
consultation – Hypoglycemia pulmonary)
• Prepare for – Hypothermia – Trauma
cardioversion
■ Figure 27-4 Algorithm for tachycardia. Boxes 9, 10, 11, 13, and 14 are designed for in-hospital use with expert
consultation available. (From American Heart Association [2005]. ACLS provider manual [p. 91]. Dallas, TX:
AHA.)