Page 668 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 668
54.
54.
Pa
54.
q
xd
q
q
Pa
44
e 6
44
44
g
g
e 6
g
xd
1
1 A
/09
1 A
2:0
2:0
1
1
/09
Pa
/30
6
6
M
/09
/30
M
A
LWB K34 0-c 27_ p pp638-654.qxd 6/30/09 12:01 AM Page 644 Aptara Inc.
LWB
LWBK340-c27_
27_
In
c.
c.
K34
63
63
p
8-6
0-c
27_
8-6
In
p
t
t
A
p
p
ara
ara
a
a
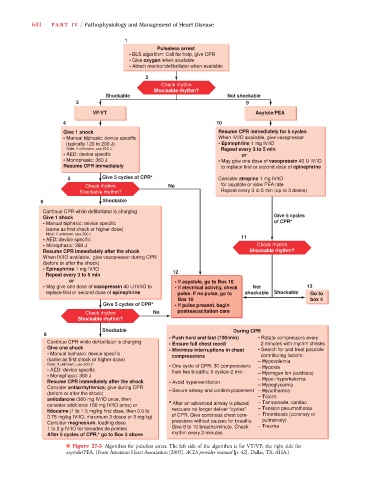
644 PA R T I V / Pathophysiology and Management of Heart Disease
1
Pulseless arrest
• BLS algorithm: Call for help, give CPR
• Give oxygen when available
• Attach monitor/defibrillator when available
2
Check rhythm
Shockable rhythm?
Shockable Not shockable
3 9
VF/VT Asytole/PEA
4 10
Give 1 shock Resume CPR immediately for 5 cycles
• Manual blphasic: device specific When IV/IO available, give vasopressor
(typically 120 to 200.J) • Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
Note: if unknown, use 200 J Repeat every 3 to 5 min
• AED: device specific or
• Monophasic: 360 J • May give one dose of vasopressin 40 U IV/IO
Resume CPR immediately to replace first or second dose of epinephrine
5 Give 5 cycles of CPR* Consider atropine 1 mg IV/IO
Check rhythm No for asystole or slow PEA rate
Shockable rhythm? Repeat every 3 to 5 min (up to 3 doses)
6 Shockable
Continue CPR while defibrillator is charging
Give 5 cycles
Give 1 shock
• Manual biphasic: device specific of CPR*
(same as first shock or higher dose)
Note: if unknown, use 200 J
11
• AED: device specific
• Monophasic: 360 J Check rhythm
Resume CPR immediately after the shock Shockable rhythm?
When IV/IO available, give vasopressor during CPR
(before or after the shock)
• Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
Repeat every 3 to 5 min 12
or • If asystole, go to Box 10
• May give one dose of vasopressin 40 U IV/IO to • If electrical activity, check Not 13
replace first or second dose of epinephrine pulse. If no pulse, go to shockable Shockable
Box 10 box 4
Give 5 cycles of CPR* • If pulse present, begin
Check rhythm No postresuscitation care
Shockable rhythm?
Shockable During CPR
8
• Push hard and fast (100/min) • Rotate compressors every
Continue CPR while defibrillator is charging • Ensure full chest recoil 2 minutes with rhythm checks
Give one shock • Minimize interruptions in chest • Search for and treat possible
• Manual biphasic: device specific compressions contributing factors:
(same as first shock or higher dose) – Hypovolemia
Note: if unknown, use 200 J • One cycle of CPR: 30 compressions
• AED: device specific then two breaths; 5 cycles≈2 min – Hypoxia
s
s
– Hydrogen lon (acidosis)
• Monophasic: 360 J
Resume CPR immediately after the shock • Avoid hyperventilation – Hypo-/hyperkalemia
– Hypoglycemia
Consider antiarrhythmics; give during CPR
(before or after the shock) • Secure airway and confirm placement – Hypothermia
amiodarone (300 mg IV/IO once, then – Toxins
– Tamponade, cardiac
consider additional 150 mg IV/IO once) or * After an advanced airway is placed.
lidocaine (1 to 1.5 mg/kg first dose, then 0.5 to rescuers no longer deliver “cycles” – Tension pneumothorax
– Thrombosis (coronary or
0.75 mg/kg IV/IO, maximum 3 doses or 3 mg/kg) of CPR. Give continous chest com-
pressions without pauses for breaths. pulmonary)
Consider magnesium, loading dose
1 to 2 g IV/IO for torsades de pointes Give 8 to 10 breaths/minute. Check – Trauma
After 5 cycles of CPR,* go to Box 5 above rhythm every 2 minutes
■ Figure 27-3 Algorithm for pulseless arrest. The left side of the algorithm is for VT/VF; the right side for
asystole/PEA. (From American Heart Association [2005]. ACLS provider manual [p. 42]. Dallas, TX: AHA.)