Page 709 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 709
09
g
P
Ap
685
5-7
qxd
04.
49
AM
/1/
7
tar
0-c
K34
p65
28_
LWB K34 0-c 28_ p65 5-7 04. qxd 7 /1/ 09 9: 49 AM P a a g e e 685 Ap tar a a
L L LWB
LWBK340-c28_p655-704.qxd 7/1/09 9:9:49 AM Page 685 Aptara
C HAPTER 2 8 / Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators 685
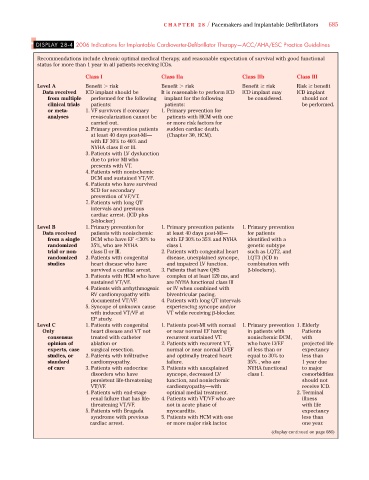
DISPLAY 28-4 2006 Indications for Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Therapy—ACC/AHA/ESC Practice Guidelines
Recommendations include chronic optimal medical therapy, and reasonable expectation of survival with good functional
status for more than 1 year in all patients receiving ICDs.
Class I Class IIa Class IIb Class III
Level A Benefit risk Benefit risk Benefit risk Risk benefit
Data received ICD implant should be It is reasonable to perform ICD ICD implant may ICD implant
from multiple performed for the following implant for the following be considered. should not
clinical trials patients: patients: be performed.
or meta- 1. VF survivors if coronary 1. Primary prevention for
analyses revascularization cannot be patients with HCM with one
carried out. or more risk factors for
2. Primary prevention patients sudden cardiac death.
at least 40 days post-MI— (Chapter 30, HCM).
with EF 30% to 40% and
NYHA class II or III.
3. Patients with LV dysfunction
due to prior MI who
presents with VT.
4. Patients with nonischemic
DCM and sustained VT/VF.
6. Patients who have survived
SCD for secondary
prevention of VF/VT.
7. Patients with long QT
intervals and previous
cardiac arrest. (ICD plus
-blocker)
Level B 1. Primary prevention for 1. Primary prevention patients 1. Primary prevention
Data received patients with nonischemic at least 40 days post-MI— for patients
from a single DCM who have EF 30% to with EF 30% to 35% and NYHA identified with a
randomized 35%, who are NYHA class I. genetic subtype
trial or non- class II or III. 2. Patients with congenital heart such as LQT2, and
randomized 2. Patients with congenital disease, unexplained syncope, LQT3 (ICD in
studies heart disease who have and impaired LV function. combination with
survived a cardiac arrest. 3. Patients that have QRS -blockers).
3. Patients with HCM who have complex of at least 120 ms, and
sustained VT/VF. are NYHA functional class III
4. Patients with arrhythmogenic or IV when combined with
RV cardiomyopathy with biventricular pacing.
documented VT/VF. 4. Patients with long QT intervals
5. Syncope of unknown cause experiencing syncope and/or
with induced VT/VF at VT while receiving -blocker.
EP study.
Level C 1. Patients with congenital 1. Patients post-MI with normal 1. Primary prevention 1. Elderly
Only heart disease and VT not or near normal EF having in patients with Patients
consensus treated with catheter recurrent sustained VT. nonischemic DCM, with
opinion of ablation or 2. Patients with recurrent VT, who have LVEF projected life
experts, case surgical resection. normal or near normal LVEF of less than or expectancy
studies, or 2. Patients with infiltrative and optimally treated heart equal to 30% to less than
standard cardiomyopathy. failure. 35% , who are 1 year due
of care 3. Patients with endocrine 3. Patients with unexplained NYHA functional to major
disorders who have syncope, decreased LV class I. comorbidities
persistent life-threatening function, and nonischemic should not
VT/VF. cardiomyopathy—with receive ICD.
4. Patients with end-stage optimal medial treatment. 2. Terminal
renal failure that has life- 4. Patients with VT/VF who are illness
threatening VT/VF. not in acute phase of with life
5. Patients with Brugada myocarditis. expectancy
syndrome with previous 5. Patients with HCM with one less than
cardiac arrest. or more major risk factor. one year.
(display continued on page 686)