Page 713 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 713
04.
qxd
7
P
5-7
tar
/1/
Ap
689
g
09
49
AM
p65
K34
0-c
28_
LWBK340-c28_p655-704.qxd 7/1/09 9:9:49 AM Page 689 Aptara
LWB K34 0-c 28_ p65 5-7 04. qxd 7 /1/ 09 9: 49 AM P a a g e e 689 Ap tar a a
LWB
C HAPTER 2 8 / Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators 689
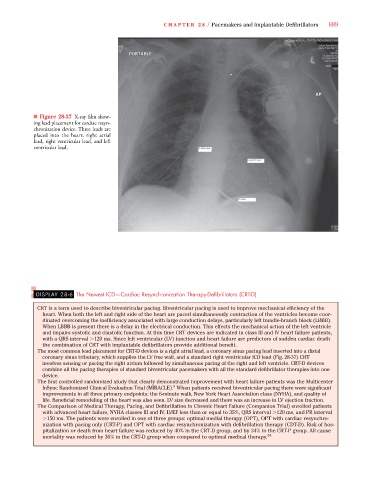
■ Figure 28-37 X-ray film show-
ing lead placement for cardiac resyn-
chronization device. Three leads are
placed into the heart; right atrial
lead, right ventricular lead, and left
ventricular lead.
DISPLAY 28-6 The Newest ICD—Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy-Defibrillators (CRT-D)
CRT is a term used to describe biventricular pacing. Biventricular pacing is used to improve mechanical efficiency of the
heart. When both the left and right side of the heart are paced simultaneously contraction of the ventricles become coor-
dinated overcoming the inefficiency associated with large conduction delays, particularly left bundle-branch block (LBBB).
When LBBB is present there is a delay in the electrical conduction. This effects the mechanical action of the left ventricle
and impairs systolic and diastolic function. At this time CRT devices are indicated in class III and IV heart failure patients,
with a QRS interval 120 ms. Since left ventricular (LV) function and heart failure are predictors of sudden cardiac death
the combination of CRT with implantable defibrillators provide additional benefit.
The most common lead placement for CRT-D devices is a right atrial lead, a coronary sinus pacing lead inserted into a distal
coronary sinus tributary, which supplies the LV free wall, and a standard right ventricular ICD lead (Fig. 28-37) CRT
involves sensing or pacing the right atrium followed by simultaneous pacing of the right and left ventricle. CRT-D devices
combine all the pacing therapies of standard biventricular pacemakers with all the standard defibrillator therapies into one
device.
The first controlled randomized study that clearly demonstrated improvement with heart failure patients was the Multicenter
6
InSync Randomized Clinical Evaluation Trial (MIRACLE). When patients received biventricular pacing there were significant
improvements in all three primary endpoints: the 6-minute walk, New York Heart Association class (NYHA), and quality of
life. Beneficial remodeling of the heart was also seen. LV size decreased and there was an increase in LV ejection fraction.
The Comparison of Medical Therapy, Pacing, and Defibrillation in Chronic Heart Failure (Companion Trial) enrolled patients
with advanced heart failure, NYHA classes III and IV, LVEF less than or equal to 35%, QRS interval 120 ms, and PR interval
150 ms. The patients were enrolled in one of three groups: optimal medial therapy (OPT), OPT with cardiac resynchro-
nization with pacing only (CRT-P) and OPT with cardiac resynchronization with defibrillation therapy (CDT-D). Risk of hos-
pitalization or death from heart failure was reduced by 40% in the CRT-D group, and by 34% in the CRT-P group. All cause
mortality was reduced by 36% in the CRT-D group when compared to optimal medical therapy. 34