Page 108 - untitled
P. 108
AAAC47 21/5/05 10:53 AM Page 107
Nerve to vastus medialis
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Saphenous nerve
Vastus medialis
Sartorius Iliotibial tract
Femoral vessels
Vastus intermedius
Great saphenous vein
Sciatic nerve
Adductor longus
Profunda vessels
Short
Gracilis heads of biceps
Long
Adductor brevis
Semimembranosus
Adductor magnus
Semitendinosus
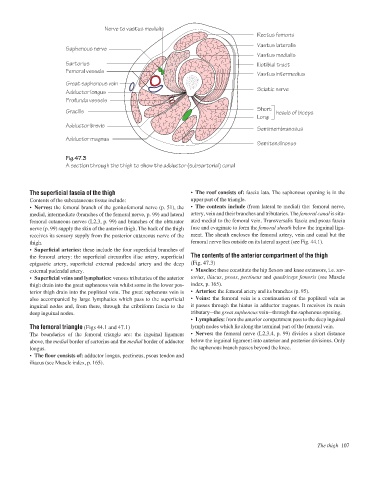
Fig.47.3
A section through the thigh to show the adductor (subsartorial) canal
The superficial fascia of the thigh • The roof consists of: fascia lata. The saphenous opening is in the
Contents of the subcutaneous tissue include: upper part of the triangle.
• Nerves: the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve (p. 51), the • The contents include (from lateral to medial) the: femoral nerve,
medial, intermediate (branches of the femoral nerve, p. 99) and lateral artery, vein and their branches and tributaries. The femoral canal is situ-
femoral cutaneous nerves (L2,3, p. 99) and branches of the obturator ated medial to the femoral vein. Transversalis fascia and psoas fascia
nerve (p. 99) supply the skin of the anterior thigh. The back of the thigh fuse and evaginate to form the femoral sheath below the inguinal liga-
receives its sensory supply from the posterior cutaneous nerve of the ment. The sheath encloses the femoral artery, vein and canal but the
thigh. femoral nerve lies outside on its lateral aspect (see Fig. 44.1).
• Superficial arteries: these include the four superficial branches of
the femoral artery: the superficial circumflex iliac artery, superficial The contents of the anterior compartment of the thigh
epigastric artery, superficial external pudendal artery and the deep (Fig. 47.3)
external pudendal artery. • Muscles: these constitute the hip flexors and knee extensors, i.e. sar-
• Superficial veins and lymphatics: venous tributaries of the anterior torius, iliacus, psoas, pectineus and quadriceps femoris (see Muscle
thigh drain into the great saphenous vein whilst some in the lower pos- index, p. 165).
terior thigh drain into the popliteal vein. The great saphenous vein is • Arteries: the femoral artery and its branches (p. 95).
also accompanied by large lymphatics which pass to the superficial • Veins: the femoral vein is a continuation of the popliteal vein as
inguinal nodes and, from there, through the cribriform fascia to the it passes through the hiatus in adductor magnus. It receives its main
deep inguinal nodes. tributaryathe great saphenous veinathrough the saphenous opening.
• Lymphatics: from the anterior compartment pass to the deep inguinal
The femoral triangle (Figs 44.1 and 47.1) lymph nodes which lie along the terminal part of the femoral vein.
The boundaries of the femoral triangle are: the inguinal ligament • Nerves: the femoral nerve (L2,3,4, p. 99) divides a short distance
above, the medial border of sartorius and the medial border of adductor below the inguinal ligament into anterior and posterior divisions. Only
longus. the saphenous branch passes beyond the knee.
• The floor consists of: adductor longus, pectineus, psoas tendon and
iliacus (see Muscle index, p. 165).
The thigh 107