Page 109 - untitled
P. 109
AAAC47 21/5/05 10:53 AM Page 108
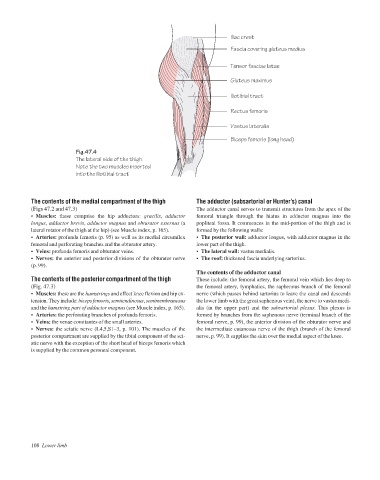
Iliac crest
Fascia covering gluteus medius
Tensor fasciae latae
Gluteus maximus
Iliotibial tract
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Biceps femoris (long head)
Fig.47.4
The lateral side of the thigh.
Note the two muscles inserted
into the iliotibial tract
The contents of the medial compartment of the thigh The adductor (subsartorial or Hunter’s) canal
(Figs 47.2 and 47.3) The adductor canal serves to transmit structures from the apex of the
• Muscles: these comprise the hip adductors: gracilis, adductor femoral triangle through the hiatus in adductor magnus into the
longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus and obturator externus (a popliteal fossa. It commences in the mid-portion of the thigh and is
lateral rotator of the thigh at the hip) (see Muscle index, p. 165). formed by the following walls:
• Arteries: profunda femoris (p. 95) as well as its medial circumflex • The posterior wall: adductor longus, with adductor magnus in the
femoral and perforating branches and the obturator artery. lower part of the thigh.
• Veins: profunda femoris and obturator veins. • The lateral wall: vastus medialis.
• Nerves: the anterior and posterior divisions of the obturator nerve • The roof: thickened fascia underlying sartorius.
(p. 99).
The contents of the adductor canal
The contents of the posterior compartment of the thigh These include: the femoral artery, the femoral vein which lies deep to
(Fig. 47.3) the femoral artery, lymphatics, the saphenous branch of the femoral
• Muscles: these are the hamstrings and effect knee flexion and hip ex- nerve (which passes behind sartorius to leave the canal and descends
tension. They include: biceps femoris,semitendinosus,semimembranosus the lower limb with the great saphenous vein), the nerve to vastus medi-
and the hamstring part of adductor magnus (see Muscle index, p. 165). alis (in the upper part) and the subsartorial plexus. This plexus is
• Arteries: the perforating branches of profunda femoris. formed by branches from the saphenous nerve (terminal branch of the
• Veins: the venae comitantes of the small arteries. femoral nerve, p. 99), the anterior division of the obturator nerve and
• Nerves: the sciatic nerve (L4,5,S1–3, p. 101). The muscles of the the intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh (branch of the femoral
posterior compartment are supplied by the tibial component of the sci- nerve, p. 99). It supplies the skin over the medial aspect of the knee.
atic nerve with the exception of the short head of biceps femoris which
is supplied by the common peroneal component.
108 Lower limb