Page 210 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 210
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 187
AP of a
Electrical activity of the heart cell
ventricular
myocardial
ECG Repolarisation
Depolarisation
Mitral Aortic Aortic Mitral
valve valve valve valve
closes opens closes opens
Heart status
Isovolumic contraction Isovolumic relaxation
Slow Atrial Rapid Reduced Rapid Slow
filling systole ejection ejection filling filling
120
Aortic pressure
100
Pressure (mmHg) 80 Left ventricular
pressure
60
Left atrial
40
20 pressure
0
a c v
wave wave wave
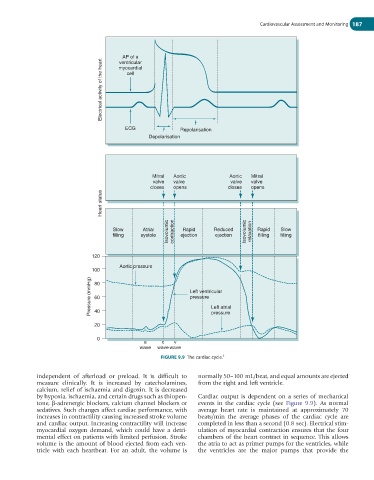
FIGURE 9.9 The cardiac cycle. 5
independent of afterload or preload. It is difficult to normally 50–100 mL/beat, and equal amounts are ejected
measure clinically. It is increased by catecholamines, from the right and left ventricle.
calcium, relief of ischaemia and digoxin. It is decreased
by hypoxia, ischaemia, and certain drugs such as thiopen- Cardiac output is dependent on a series of mechanical
tone, β-adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers or events in the cardiac cycle (see Figure 9.9). As normal
sedatives. Such changes affect cardiac performance, with average heart rate is maintained at approximately 70
increases in contractility causing increased stroke volume beats/min the average phases of the cardiac cycle are
and cardiac output. Increasing contractility will increase completed in less than a second (0.8 sec). Electrical stim-
myocardial oxygen demand, which could have a detri- ulation of myocardial contraction ensures that the four
mental effect on patients with limited perfusion. Stroke chambers of the heart contract in sequence. This allows
volume is the amount of blood ejected from each ven- the atria to act as primer pumps for the ventricles, while
tricle with each heartbeat. For an adult, the volume is the ventricles are the major pumps that provide the