Page 353 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 353
330 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
9
when administering oxygen so that the stimulus to blood. Other receptors include stretch receptors located
breathe is not compromised, as increases in PO 2 may in the lungs that inhibit inspiration and protect the lungs
reduce respiratory drive. Peripheral chemoreceptors from over-inflation (Hering–Breuer reflex), and in the
respond to low partial pressure of oxygen in arterial muscles and joints (see Figure 13.7).
blood (PaO 2 ) and contribute to maintaining ventilation,
functioning optimally when oxygen levels fall below PULMONARY VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
70 mmHg. 7 In healthy individuals, the lungs are readily distensible
Central chemoreceptors located in the medulla respond or compliant; when exposed to high expanding pressures
to changes in hydrogen ion concentration in the CSF that or in disease states, compliance is increased or decreased.
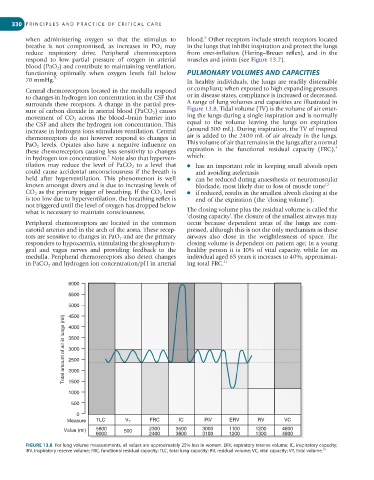
surrounds these receptors. A change in the partial pres- A range of lung volumes and capacities are illustrated in
sure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO 2 ) causes Figure 13.8. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air enter-
movement of CO 2 across the blood–brain barrier into ing the lungs during a single inspiration and is normally
the CSF and alters the hydrogen ion concentration. This equal to the volume leaving the lungs on expiration
increase in hydrogen ions stimulates ventilation. Central (around 500 mL). During inspiration, the TV of inspired
chemoreceptors do not however respond to changes in air is added to the 2400 mL of air already in the lungs.
PaO 2 levels. Opiates also have a negative influence on This volume of air that remains in the lungs after a normal
4
these chemoreceptors causing less sensitivity to changes expiration is the functional residual capacity (FRC),
in hydrogen ion concentration. Note also that hyperven- which:
7
tilation may reduce the level of PaCO 2 to a level that ● has an important role in keeping small alveoli open
could cause accidental unconsciousness if the breath is and avoiding atelectasis
held after hyperventilation. This phenomenon is well ● can be reduced during anaesthesia or neuromuscular
known amongst divers and is due to increasing levels of blockade, most likely due to loss of muscle tone 12
CO 2 as the primary trigger of breathing. If the CO 2 level ● if reduced, results in the smallest alveoli closing at the
is too low due to hyperventilation, the breathing reflex is end of the expiration (the ‘closing volume’).
not triggered until the level of oxygen has dropped below
what is necessary to maintain consciousness. The closing volume plus the residual volume is called the
‘closing capacity’. The closure of the smallest airways may
Peripheral chemoreceptors are located in the common occur because dependent areas of the lungs are com-
carotid arteries and in the arch of the aorta. These recep- pressed, although this is not the only mechanism as these
tors are sensitive to changes in PaO 2 and are the primary airways also close in the weightlessness of space. The
responders to hypoxaemia, stimulating the glossypharyn- closing volume is dependent on patient age; in a young
geal and vagus nerves and providing feedback to the healthy person it is 10% of vital capacity, while for an
medulla. Peripheral chemoreceptors also detect changes individual aged 65 years it increases to 40%, approximat-
in PaCO 2 and hydrogen ion concentration/pH in arterial ing total FRC. 11
6000
5500
5000
4500
Total amount of air in lungs (ml) 3500
4000
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
Measure TLC V T FRC IC IRV ERV RV VC
Value (ml) 5800 500 2300 3500 3000 1100 1200 4600
6000 2400 3600 3100 1200 1300 4800
FIGURE 13.8 For lung volume measurements, all values are approximately 25% less in women. ERV, expiratory reserve volume; IC, inspiratory capacity;
10
IRV, inspiratory reserve volume; FRC, functional residual capacity; TLC, total lung capacity; RV, residual volume; VC, vital capacity; VT, tidal volume.