Page 420 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 420
Ventilation and Oxygenation Management 397
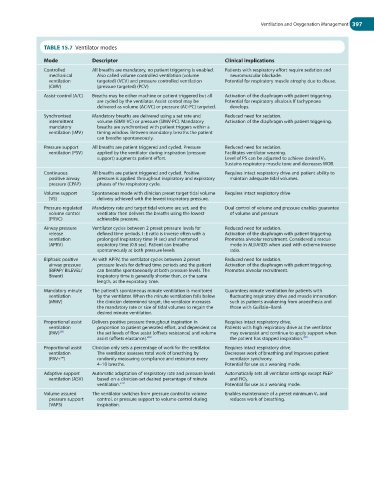
TABLE 15.7 Ventilator modes
Mode Descriptor Clinical implications
Controlled All breaths are mandatory, no patient triggering is enabled. Patients with respiratory effort require sedation and
mechanical Also called volume controlled ventilation (volume neuromuscular blockade.
ventilation targeted) (VCV) and pressure controlled ventilation Potential for respiratory muscle atrophy due to disuse.
(CMV) (pressure targeted) (PCV)
Assist-control (A/C) Breaths may be either machine or patient triggered but all Activation of the diaphragm with patient triggering.
are cycled by the ventilator. Assist control may be Potential for respiratory alkalosis If tachypnoea
delivered as volume (AC-VC) or pressure (AC-PC) targeted. develops.
Synchronised Mandatory breaths are delivered using a set rate and Reduced need for sedation.
intermittent volume (SIMV-VC) or pressure (SIMV-PC). Mandatory Activation of the diaphragm with patient triggering.
mandatory breaths are synchronised with patient triggers within a
ventilation (IMV) timing window. Between mandatory breaths the patient
can breathe spontaneously.
Pressure support All breaths are patient triggered and cycled. Pressure Reduced need for sedation.
ventilation (PSV) applied by the ventilator during inspiration (pressure Facilitates ventilator weaning.
support) augments patient effort. Level of PS can be adjusted to achieve desired V T .
Sustains respiratory muscle tone and decreases WOB.
Continuous All breaths are patient triggered and cycled. Positive Requires intact respiratory drive and patient ability to
positive airway pressure is applied throughout inspiratory and expiratory maintain adequate tidal volumes.
pressure (CPAP) phases of the respiratory cycle.
Volume support Spontaneous mode with clinician preset target tidal volume Requires intact respiratory drive
(VS) delivery achieved with the lowest inspiratory pressure.
Pressure-regulated Mandatory rate and target tidal volume are set, and the Dual control of volume and pressure enables guarantee
volume control ventilator then delivers the breaths using the lowest of volume and pressure
(PRVC) achievable pressure.
Airway pressure Ventilator cycles between 2 preset pressure levels for Reduced need for sedation.
release defined time periods. I : E ratio is inverse often with a Activation of the diaphragm with patient triggering.
ventilation prolonged Inspiratory time (4 sec) and shortened Promotes alveolar recruitment. Considered a rescue
(APRV) expiratory time (0.8 sec). Patient can breathe mode in ALI/ARDS when used with extreme inverse
spontaneously at both pressure levels ratio.
Biphasic positive As with APRV, the ventilator cycles between 2 preset Reduced need for sedation.
airway pressure pressure levels for defined time periods and the patient Activation of the diaphragm with patient triggering.
(BiPAP/ BILEVEL/ can breathe spontaneously at both pressure levels. The Promotes alveolar recruitment.
Bivent) inspiratory time is generally shorter than, or the same
length, as the expiratory time.
Mandatory minute The patient’s spontaneous minute ventilation is monitored Guarantees minute ventilation for patients with
ventilation by the ventilator. When the minute ventilation falls below fluctuating respiratory drive and muscle innervation
(MMV) the clinician determined target, the ventilator increases such as patients awakening from anaesthesia and
the mandatory rate or size of tidal volumes to regain the those with Guillain–Barré.
desired minute ventilation.
Proportional assist Delivers positive pressure throughout inspiration in Requires intact respiratory drive.
ventilation proportion to patient generated effort, and dependent on Patients with high respiratory drive as the ventilator
(PAV) 269 the set levels of flow assist (offsets resistance) and volume may overassist and continue to apply support when
assist (offsets elastance). 268 the patient has stopped inspiration. 269
Proportional assist Clinician only sets a percentage of work for the ventilator. Requires intact respiratory drive.
ventilation The ventilator assesses total work of breathing by Decreases work of breathing and improves patient
(PAV+™) randomly measuring compliance and resistance every ventilator synchrony.
4–10 breaths. Potential for use as a weaning mode.
Adaptive support Automatic adaptation of respiratory rate and pressure levels Automatically sets all ventilator settings except PEEP
ventilation (ASV) based on a clinician-set desired percentage of minute and FiO 2 .
ventilation. 270 Potential for use as a weaning mode.
Volume assured The ventilator switches from pressure control to volume Enables maintenance of a preset minimum V T and
pressure support control, or pressure support to volume control during reduces work of breathing.
(VAPS) inspiration.