Page 423 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 423
400 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
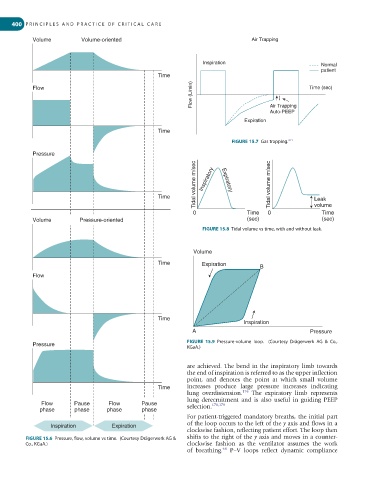
Volume Volume-oriented Air Trapping
Inspiration Normal
patient
Time
Flow (L/min) }
Flow Time (sec)
Air Trapping
Auto-PEEP
Expiration
Time
FIGURE 15.7 Gas trapping.
271
Pressure
Tidal volume m/sec Inspiratory Expiratory Tidal volume m/sec
Time Leak
0 Time 0 volume
Time
Volume Pressure-oriented (sec) (sec)
FIGURE 15.8 Tidal volume vs time, with and without leak.
Volume
Time Expiration B
Flow
Time
Inspiration
A Pressure
Pressure FIGURE 15.9 Pressure-volume loop. (Courtesy Drägerwerk AG & Co.,
KGaA.)
are achieved. The bend in the inspiratory limb towards
the end of inspiration is referred to as the upper inflection
point, and denotes the point at which small volume
Time increases produce large pressure increases indicating
lung overdistension. 176 The expiratory limb represents
lung derecruitment and is also useful in guiding PEEP
Flow Pause Flow Pause selection. 178,179
phase phase phase phase
For patient-triggered mandatory breaths, the initial part
Inspiration Expiration of the loop occurs to the left of the y axis and flows in a
clockwise fashion, reflecting patient effort. The loop then
FIGURE 15.6 Pressure, flow, volume vs time. (Courtesy Drägerwerk AG & shifts to the right of the y axis and moves in a counter-
Co., KGaA.) clockwise fashion as the ventilator assumes the work
68
of breathing. P–V loops reflect dynamic compliance